Large time behavior of solutions for a complex-valued quadratic heat equation
|
|
|
- Tove Astrup
- 4 år siden
- Visninger:
Transkript
1 Nonlinear Differ. Equ. Appl. 5, 5 45 c 5 Springer Basel -97/5/55-4 published online March 5, 5 DOI.7/s Nonlinear Differenial Equaions and Applicaions NoDEA Large ime behavior of soluions for a complex-valued quadraic hea equaion Amel Chouichi, Sarah Osmane and Slim Tayachi Absrac. In his paper we sudy he exisence and he asympoic behavior of global soluions for a parabolic sysem relaed o he complexvalued hea equaion wih quadraic nonlineariy: z =Δz + z,>, x R N, wih iniial daa z = u + iv. We show ha if u x c x α and v x c x α, as x wih α, α α N N α, α >, > c is sufficienly small, hen he soluion is global and converges o a self-similar soluion. We also esablish he exisence of four differen self-similar behaviors. These behaviors depend on he values of α and α. In paricular, he real and he imaginary pars of he consruced soluions may have differen behaviors in he L -norm for large ime. Also, he real par may have differen behaviors from hose known for he real-valued quadraic hea equaion. Mahemaics Subjec Classificaion. 35K5, 35K55, 35K65, 35B4. Keywords. Parabolic sysem, Semi-linear parabolic equaions, Global soluions, Large ime behavior, Self-similar soluions, Nonlinear hea equaion.. Inroducion In his paper we consider he complex-valued nonlinear hea equaion: z =Δz + z,. z = z,. where z = z, x is a complex valued funcion, >, x R N, and he iniial condiion z x is a complex valued funcion defined on R N. The aim of his paper is o prove he exisence of global soluions for. and sudy heir asympoic behavior, as, for a class of iniial daa z. In paricular, we consider z = u +iv, where u,v are given precisely in he space L R N CR N bu no in he space L R N. Equaion. has a srong relaion wih he viscous Consanin Lax Majda equaion. See and reference herein. If we wrie z, x = u, x +
2 6 A. Chouichi, S. Osmane and S. Tayachi NoDEA iv, x, where i =, hen he above equaion is rewrien as he parabolic sysem: { u =Δu + u v,.3 v =Δv +uv, u = u,v = v..4 In he case where z is real-valued, ha is v, hen he previous sysem is reduced o he scalar quadraic hea equaion u =Δu + u,.5 where u = u, x is a real valued funcion, >, x R N. In,8, i is proved ha if he iniial value u c x α, as x wih c is a small consan, N>αand α, hen he soluion u of.5 is global and is asympoic, in some Lebesgue spaces, o a self-similar soluion of.5 ifα =, and is asympoic o e Δ c x α ifα>, where e Δ is he hea semigroup. Moreover, in 8 i is proved ha he asympoic behavior holds in he L -norm. Furhermore, he resuling soluion u saisfies, for large, u α,α. The exisence of self-similar soluions of.5 wih iniial daa u x =c x is proved in. See also 5. We refer he reader o he paper 8 for more relaed resuls on he Eq..5. Many resuls have been esablished concerning exisence of self-similar soluions and asympoically self-similar soluions for oher sysems using he mehods used in, 8. In 6, he semi-linear parabolic sysem wih nonlinear erms of he form a j u pj u + b j v qj v, p j,q j >, a j, b j R, j =,, have been sudied. The global exisence and he exisence of asympoically self-similar soluion are shown under some condiions on he parameers. In 7, he semi-linear parabolic sysem wih produc nonlinear erms of he form a j u pj u v qj v, where a j R and p j,q j, j=,. If we rea he Eq.. asin,8, we obain similar resuls as in,8 on he behavior of z. Bu, his will no show he difference on he behavior of he real and he imaginary par of he soluion. On he oher hand, he sysem.3 is no sudied neiher in 6 nor in 7. In fac, he case where he sum and he produc are in he same sysem is no considered. The aim of his paper is o sudy he large ime behavior of global soluions for he sysem.3. The Cauchy problem for he sysem.3 wih an iniial daa u,v L R N CR N,.6 has a unique soluion u, v C,T; L R N, where T = T u,v, denoes he maximal exisence ime of he soluion. Moreover, we have eiher T =, or T< and lim { u., + v., } =..7 T The sysem.3 has been sudied in 3. In paricular, global exisence resuls and large ime behavior are esablished under some appropriae condiions on iniial values. More precisely, he auhors show ha if he iniial daa u,v saisfy for all x R N
3 Vol. 5 The complex valued nonlinear hea equaion 7 u x Av x <,.8 wih A R is a consan, hen, he soluion of.3 saisfying.6 exiss globally in ime. See 3, Theorem., p.. Moreover, in 3 he auhors sudy he large ime behavior for he case where he iniial daa are posiive and asympoically consans. More precisely, hey impose he following condiions on iniial daa: u,v C R N, u N,u N, v L, L >,.9 lim u x =N, lim v x =N,N >N >,. x x and hey prove ha he soluions converges o he saionary soluions of.3. See 3, Theorem.4, p. 4. In he presen paper, a differen class of iniial values are considered. In paricular, we do no impose a resricion on he sign of he iniial daa. Also, we do no consider he condiions.8 and.9. In our case. is saisfied for N = N =. We have obained he following heorem. Theorem.. Global exisence Le N be an ineger, α and α be posiive real numbers saisfying α and α α. Suppose ha N N >, α α >. Consider u,v L R N CR N be such ha u c η x α, v c η x α,. where η is an L cu-off funcion η near he origin and having a compac por. Then, here exiss ε> such ha if max c, c <ε, he soluion of.3 wih iniial daa u,v exiss globally in ime. The case of α = α is proved in,8. In fac, alhough in,8 only he real valued nonlinear hea equaion is considered, bu he case α = α can be proved using exacly he same calculaions of, 8. Tha is by working direcly on he Eq... Our resul is new for α α. For general formulaion see Theorem.6 below. The mehod which we have employed is differen from 3. Our ideas are based on he echnique used in,6 8. The exisence of self-similar soluions for he sysem.3, ha is., has been proved in. I is proved here ha if u = c x, v = c x, c sufficienly small, hen here exiss a self-similar soluion of he sysem.3. Similar calculaions, give he exisence of a self-similar soluion of he sysem.3 wih iniial daa c x,c x, wih c,c are wo small consans. In order o sudy he differen asympoic behaviors of global soluions for he sysem.3, we consruc self-similar soluions for he following asympoic sysem: { w =Δw + w,. w =Δw +w w, where w, x andw, x are real valued funcions, >, x R N.Wehus have he following heorem.
4 8 A. Chouichi, S. Osmane and S. Tayachi NoDEA Figure. Asympoic behavior. Assume he condiion on α,α : α, α α, α,α <N/. If α α > wih α >, hen, we have LB for z case i. If α,α are on he line passing hrough he poins,.5 and, wih α >, hen, we have LNLB for Rez, LB for Imz case ii. If α,α are on he line passing hrough he poins, and, wih α >, hen, we have LB for Rez, NLB for Imz case iii. Finally, if α,α =,, we have NLB for z case iv. Where LB linear behavior, LNLB linear and nonlocal behavior, NLB nonlinear behavior Theorem.. Self-similar soluions Le N be an ineger, α be posiive real number saisfying α N >, >. Consider u = c x, v = c x α. Then, here exiss ε> such ha if max c, c <ε, here exiss a global self-similar soluion for he sysem w =e Δ c x + α e sδ w s ds,.3 w =e Δ c x α + e sδ w sw s ds..4 See Theorem 3.3 below for he general version of he previous resul. In his paper we also discuss all possible asympoic self-similar behaviors for he sysem.3 which are described in he heorem below and illusraed by he Fig.. Theorem.3. Differen asympoic behavior Le N be an ineger, α and α be wo real numbers saisfying
5 Vol. 5 The complex valued nonlinear hea equaion 9 α, α N N α, > and α α >. Le U =u, v be he global soluion of.3 wih iniial value ηu,v consruced by Theorem., u = c x α,v = c x α such ha max c, c <ε.hereη and ε are as in Theorem.. Then, for ε sufficienly small, here exiss a real number δ >, such ha for all δ saisfying <δ<δ, here exiss a posiive consan C δ such ha he following holds: i If α > and α >α +, we have u e Δ c x α C δ α δ, >,.5 v e Δ c x α C δ α δ, >..6 ii If α > and α = α +, we have u e Δ c x α +g C δ α δ, >,.7 v e Δ c x α C δ α δ, >,.8 where g = e sδ e sδ c x α ds. iii If α =and α >, we have u w C δ δ, >,.9 v w C δ α δ, >,. wih w and w are given by.3.4. Moreover, in all cases he resuling soluion u, v saisfies, for large d α u d α, d α v d α,. where d,d are posiive consans. Remark.4. Using he mehod in,8, we prove ha, if α = α =,we have u w C δ δ, >,. v w C δ δ, >,.3 wih w and w are he self-similar soluion of sysem.3 wih iniial daa c x,c x. I follows from he previous resul ha, he consruced soluion u, v is asympoically self-similar in he L L norm. See Theorem 4. below for general version of he previous Theorem. The case α = α and c = c is proved in,8. Also, for he case c c he resul of,8 can be exended wih minor modificaion. The case α α is new. Noe ha he real par of he complex-valued hea equaion and he real-valued hea equaion behave differenly. In paricular, he behaviors ii and iii can no hold for he realvalued quadraic hea equaion. This shows he influence of he imaginary par
6 A. Chouichi, S. Osmane and S. Tayachi NoDEA Figure. Comparison beween he L -norm of he real and he imaginary pars for large ime. In he shaded region: α > α and α α +, we have Rez Imz. In he Hached region: α < α and α, we have Imz Rez. On he line α = α, we have Imz Rez on he large ime behavior of he real par. For α >, we have ha if α >α he imaginary par v dominaes he real par u, as in he L -norm while if + α α <α he real par u dominaes he imaginary par v Fig.. For blowing up soluions, in 4 a simulaneously blowing up soluion for he sysem.3 is consruced such ha he real par u and he imaginary par v of z blow up simulaneously a x = and such ha he real par dominaes he imaginary par. Le us poin also ha he previous asympoic behavior is no described in 3. Moreover, he convergence resuls in 3 is proved under he assumpions.9,.. Remark.5. By he previous resul we have he following comparison beween he real par and he imaginary par of he soluion: i If α and α = α, for large ime, we have u α and v α, so, he real par Rez and he imaginary par Imz have he same behavior as and we wrie Rez Imz. ii If α > andα >α, here we noe ha he real par Rez dominaes he imaginary par Imz and we wrie Imz Rez. iii If α >, α α andα <α, here we noe ha he imaginary par Imz dominaes he real par Rez and we wrie Rez Imz.
7 Vol. 5 The complex valued nonlinear hea equaion In his work we sudy he global exisence and he differen asympoic behaviors of mild global soluions for he following general parabolic sysem { u =Δu + au + bv,.4 v =Δv + cuv, wih iniial value u,x=u x, v,x=v x,.5 where u, x andv, x are real valued funcions, >, x R N,a,b,c R. Noe ha sysem.4 is a generalizaion of he following equaion z =Δz + az,.6 for >, x R N and wih iniial daa z = u + iv,a R and b = a, c = a. By he well-known Duhamel formulaion, we see ha he problem can be furher reduced ino he following sysem of inegral equaions. u =e Δ u + a v =e Δ v + c e sδ u sds + b e sδ v s ds,.7 e sδ usvs ds,.8 where e Δ is he hea operaor which can be regarded as he convoluion wih he hea kernel. The mehod inroduced by, 6 8 uses he inegral formulaion of he semi-linear equaion or sysem under sudy. So, laer on we will work on he above sysem of inegral equaions insead of.4. The firs sep is o prove he exisence and uniqueness of global soluions for he inegral formulaion.7.8 in some funcional spaces, and allowing o use a suiable conracion mapping argumen on he whole ime inerval,. Second, we will consruc self-similar soluions for he corresponding asympoic sysem of.4: w =Δw + aμw + bνw,.9 w =Δw + cμw w,.3 where w, x andw, x are real valued funcions, >,x R N,a,b,c are he same parameers as in sysem.4. The parameers μ and ν are defined by μ = lim s s α, ν = lim s s α α..3 In reaing self-similar soluions, we shall use he sandard mehod inroduced in 6 see also,7,8. From he scaling principe, i is easy o see ha if u, x,v, x are a soluions of he Cauchy problem.4, hen, he rescaled funcions u λ, x =λ α uλ, λx, v λ, x =λ α vλ, λx, λ >,.3 are also a soluion of he sysem.4 wih iniial value u λ,x=λ α u λx, v λ,x=λ α v λx. Then, a soluion u, v is said o be self-similar when u, x,v, x = λ α uλ, λx,λ α vλ, λx, λ >..33
8 A. Chouichi, S. Osmane and S. Tayachi NoDEA Finally, for he asympoic behavior resuls, we prove ha some of he global soluions of he sysem.7.8 are asympoic, for large ime, o selfsimilar soluions of inegral sysem relaed o.9.3 wih iniial value c x α,c x α. The res of his paper is organized as follows. In he nex secion, we presen some preliminary lemmas which will be needed in he proofs of he heorems. Furhermore, we sae and we prove he main resuls concerning he global exisence and coninuous dependence. In Sec. 3, we prove he exisence of global soluions and self-similar soluions for he asympoic sysems, also we demonsrae Theorems. and.. Finally, in Sec. 4, we sudy he asympoic behaviors for soluions of hese sysems wih small iniial values wih respec o some norm and we prove Theorem.3. In his paper, we will denoe by C a posiive consan which can be differen a differen places and also denoe i by C δ o indicae ha i depends on a real number δ. We someimes denoe u,. byu.. Global exisence Throughou his secion, we give in he firs subsecion he following resuls which will be used laer in he second subsecion for he proof of he exisence of global soluion o Technical resuls In his subsecion, we shall sae some basic facs and obain auxiliary resuls. Firs of all, for r,l r R N denoes he usual Lebesgue space on R N wih he norm. r.lee Δ be he linear hea semigroup which is defined by e Δ ϕx =G ϕx, where G is he hea kernel given by G, x = N e x 4, >, x R N,. 4π and sands for he convoluion produc. We consider α,α wo real number such ha α, α α +,. and N N α >, α >. One can choose a real number r which saisfy < α +α r < N α <r and α < α α +α r < N <r..3 α For r saisfying.3, define he real numbers r,s and s by r = α r, s = α α α r, s = α α r,.4 where α,α be wo real number saisfying α, α α +..5
9 Vol. 5 The complex valued nonlinear hea equaion 3 Now, for Φ = ϕ,ϕ S R N S R N, define N by N Φ = β e Δ ϕ r, β e Δ ϕ r, γ e Δ ϕ s, γ e Δ ϕ s, >.6 where β,β,γ and γ are given by β = α N r, γ = α N s,.7 β = α N, γ = α N..8 r s Now, we will give some preliminary lemmas which will be needed in he proofs of he main heorems. Lemma. is a direc consequence of he condiions.3.4 and.7.8. We will need some real inerpolaing number defined in he Lemma.3 which saisfy he condiions saed in Corollary.5. As well as, in he Corollary.5, he Par represen compaibiliy condiions for he hea semigroup, ha is e Δ maps beween he appropriae Lebesgue spaces. The Par is inegrabiliy condiions: o assure ha he various inegrals are convergen. Finally, Par 3 will allow he conracion mapping argumen o be done on he ime inerval, direcly. Lemma.. Le N be an ineger. Le α,α be posiive real numbers which saisfy.. Leα,α be posiive real numbers which saisfy.5. Suppose ha N N >, α α >. Le r be a real number saisfying.3 and le r,s and s be given by.4. Le β,β,γ and γ be given by.7 and.8. Then, we have he following: i <β <β, <γ <γ, ii < αj +α j r j < N α j <r j, < α j +α s j < N j α j iii +αj α j β j <, iv β j +α j α γ j <, for j =,, j N α jr j +αj α j β j +=, γ j N α j sj <s j,forj =,, +α j α γ j +=,forj =,. j Proof. The lemma follows from he expressions of r,r,s and s by a direc consequence of he condiions.3.4 and from he expressions of β,β,γ and γ concluded from he condiions.7.8. Lemma.. Le α,α,α and α be posiive real numbers, hen, hey saisfy respecively. and.5 if and only if he following condiions hold: a <α α and <α α, b α α α+ α α+ c α α α+ α α α, α < α α, α α α+ α α α. α α α + α α + α < α α,
10 4 A. Chouichi, S. Osmane and S. Tayachi NoDEA Lemma.3. Le N be an ineger. Le α,α be posiive real numbers which saisfy.. Leα,α be posiive real numbers which saisfy.5. Suppose ha N N >, α α >. Le r j,s j,β j and γ j for j =, be as in Lemma.. Then, here exiss he inerpolaing real numbers r j,β j,τ j and Γ j,j=, which are defined as follow: r j = α j r j ; β j = +α j β j ; τ j = α j +α j α j +α j s j ; Then, we have he following Γ j = +α j α j γ j. r j r,r s,s, β j β,β γ,γ, j =,. Furhermore, here exiss r j r,r,s j s,s,β j β,β and γ j γ,γ such ha = +, τ j r j s j Γ j = β j + γ j..9 Also, here exiss θ j,θ j, forj =, such ha = θ j + θ j ; r j r r β j = θ j β + θ j β,. = θ j + θ j ; r j s s β j = θ jγ + θ jγ.. Moreover, here exiss θ j,θ j,, for j =, such ha = θ j + θ j ; r j r r β j = θ j β + θ j β ; = θ j + θ j ; s j s s γ j = θ jγ + θ jγ.. Proof. Owing o he condiions.3.4 and.7.8 and Lemma., he proof of he lemma is obvious and lef o he reader. Remark.4. As a choice, we can ake, for j =, r j = s j = α j +α j s j ; β j = γ j = +α j α j γ j. As a corollary of he previous lemmas we have he following resul. Corollary.5. Le N be an ineger. Le α,α be posiive real numbers which saisfy.. Leα,α be posiive real numbers which saisfy.5. Suppose ha N N >, α α >. Le r,r,s,s,β,β,γ and γ be as in Lemma.. Ler j,τ j,β j and Γ j,j=, be as in Lemma.3. Then,forj =,, we have:
11 Vol. 5 The complex valued nonlinear hea equaion 5 < rj <r j, <τ j <s j, N β j <, r j N r j <, Γ j <, τ j s j <, 3 + β j N r j r j β j =, +γ j N τ j s j Γ j =. Proof. Owing o he condiions saisfied by r,r,s, and s in he Lemmas. and.3, and due o he expressions of β,β,γ and γ, he proof of Corollary.5 is simple and can be omied... Global exisence In his subsecion, we give he Theorem and he proof of he global exisence and coninuous dependence of soluions for he sysem.7.8. Theorem.6. Global exisence and coninuous dependence Le N be an ineger. Le α,α,α and α be posiive real numbers saisfying α, α α +, α, α α +. Suppose ha N N > and α α >. Le r be a real number saisfying.3 and le r,s and s be defined in.4 β,γ and β,γ be defined by.7 and.8 respecively. Le M>be such ha C := CM <,.3 where CM is a posiive consan given by.38 below. Choose R> such ha R + CM M..4 If Φ=ϕ,ϕ be an elemen of S R N S R N such ha N Φ R,.5 where N is given by.6, hen, here exiss a unique global soluion U =u, v of he inegral sysem.7.8 such ha > β u r, β u r, γ v s, γ v s M..6 Furhermore, a u e Δ ϕ C,,L τ R N, for αr +α <τ< N α. b v e Δ ϕ C,,L τ R N, for α s +α <τ < N α c u e Δ ϕ L,,L N α R N,v e Δ ϕ L,,L N α R N. d lim u =ϕ and lim v =ϕ in he sense of empered disribuions. Moreover, he global soluion U =u, v saisfies α N r u r, α N r u r, α N s v s, α N s v s <, > for all r r,,r r,,s s, and s s,...7
12 6 A. Chouichi, S. Osmane and S. Tayachi NoDEA In addiion, if U =u,v and U =u,v be respecively he soluions of.7.8 saisfying.6 wih iniial values Φ=ϕ,ϕ and Ψ= ψ,ψ which verify.5, hen, for all r r,,r r,,s s, and s s,, we have > β u u r, β u u r, γ v v s, γ v v s C N Φ Ψ,.8 where C is given in Theorem.6 by.38 below. Proof. We look for global mild soluions of he sysem.7.8 wih iniial daa Φ = ϕ,ϕ via a fixed poin argumen. Le X be he se of Bochner measurable funcions U :, L r R N L r R N L s R N L s R N U :=u,v such ha U X = β u r, β u r, γ v s, γ v s <..9 > Le M be a posiive real number. We denoe by X M he se of u X such ha U X M. Endowed wih he meric du,u = U U X,X M is a complee meric space. Define he mapping F Φ : X M X M by F Φ u, v =F Φ u, v,g Φ u, v,. wih F Φ u, v =e Δ ϕ +a G Φ u, v =e Δ ϕ + c e sδ u s ds + b e sδ v s ds,. e sδ usvs ds,. where Φ = ϕ,ϕ belongs o S R N S R N saisfies.5. We will show ha F Φ given by. is a sric conracion mapping on X M for suiable real numbers M and R. Le Φ = ϕ,ϕ, Ψ=ψ,ψ S R N S R N saisfies.5 andu =u,v,u =u,v be wo elemens of X M. Then, we esimae γj G Φ U G Ψ U sj and βj F Φ U F Ψ U rj, for j =,. Thus, by using he smoohing effec e Δ ϕ q C N p q ϕ p,.3 for all >,ϕ L p R N, C is a posiive consan and p q and due o Corollary.5 par, we apply.3 forp, q =τ j,s j,j =, and ϕ =u sv s u sv s, we wrie γj G Φ U G Ψ U sj γj e Δ ϕ ψ sj +C c γj s N τ j s j u sv s u sv s τj ds,.4
13 Vol. 5 The complex valued nonlinear hea equaion 7 where τ j are given by.9 forj =,. Now, we remark ha u v u v τj u v v τj + v u u τj. Due o.9, we use he following Hölder inequaliy fg τj f rj g sj,.5 for all f L rj R N andg L sj R N, o obain u v v τj + v u u τj u rj v v sj + v sj u u rj..6 Injecing.6 in.4, we have γj G Φ U G Ψ U sj γj e Δ ϕ ψ sj +C c γj s N τ j s j u s rj v s v s sj + v s sj u s u s rj ds..7 By Lemma.3, we apply on he second erm of he righ-hand side of he las inequaliy he inerpolaion inequaliy f s f θ r f θ τ, f L r R N L τ R N,.8 where r τ, s = θ r + θ, θ,, τ once wih s, r, τ =r j,r,r,θ= θ j,f = u and s, r, τ =s j,s,s, θ = θ j,f = v v,forj =, and once wih he same riple bu wih f = u u for he firs and f = v for he second, wih he fac ha U and U belongs o X M, we obain γj G Φ U G Ψ U sj γj e Δ ϕ ψ sj +MC c γj s N τ j s j s Γ j ds U U X NΦ Ψ + MC c +γj N τ j s Γ j j s N τ j s j s Γ j ds U U X..9 From properies and 3 of Corollary.5, we deduce γj G Φ U G Ψ U sj NΦ Ψ + C j U U X,.3 where C j = c MC s N τ j s j s βj+γj ds,.3 which is a finie posiive consan from propery of Corollary.5.
14 8 A. Chouichi, S. Osmane and S. Tayachi NoDEA We now esimae βj F Φ U F Ψ U rj. In fac, we have for U,U X M βj F Φ U F Ψ U rj βj e Δ ϕ ψ rj + a βj u e sδ s us ds rj + b βj v e sδ s vs ds. rj We compue, using he smoohing properies of he hea semigroup.3 wih p, q = rj,r j on he second and he hird erm of he righ-hand side of he las inequaliy and par of Corollary.5, forj =,, we have βj F Φ U F Ψ U rj βj e Δ ϕ ψ rj + a C βj s N + b C βj s N r j r j I follows by he Hölder inequaliy, ha for j =, r j u s u s rj/ ds r j v s vs rj/ ds..3 βj F Φ U F Ψ U rj βj e Δ ϕ ψ rj + a C βj s N r j + b C βj s N r j u s rj + u s rj u s u s rj ds r j r j v s rj + v s rj v s v s rj ds..33 Using Lemma.3 and he inerpolaion inequaliy.8 wih s, r, τ =r j, r,r,θ = θ j for f {u,u,u u } on he second erm of he righhand side of he las inequaliy and wih s, r, τ =r j,s,s,θ = θ j for f {v,v,v v } on he hird erm, and he fac ha U and U belongs o X M, we see ha inequaliy.33 becomes β j F Φ U F Ψ U rj NΦ Ψ + CM a + b +β j N s N β r j r j j r j r j s β j ds U U X..34 We deduce, by using he expressions of r j and β j inroduced in Lemma.3, and heir properies given in and 3 of Corollary.5 ha βj F Φ U F Ψ U rj NΦ Ψ + C j U U X,.35
15 Vol. 5 The complex valued nonlinear hea equaion 9 where C j =MC a + b s N r j r j s βj ds,.36 i follows by propery of Corollary.5 ha C j,forj =, is a finie posiive consan. So, inequaliies.3 and.35 wih j =, lead o F Φ U F Ψ U X NΦ Ψ + C U U X,.37 where C := CM = max {C j,c j,j=, }..38 Now if we ake Ψ = and U =, he inequaliy.37 becomes F Φ U X NΦ + C U X..39 If we choose M and R such ha.3 and.4 are saisfied, hen, by.39, F Φ maps X M ino iself. For Φ = Ψ,.37 becomes F Φ U F Ψ U X C U U X, hence inequaliy.3 gives ha F Φ is a sric conracion mapping from X M ino iself. So F Φ has a unique fixed poin U =u, v inx M which is he soluion of he inegral sysem.7.8. This erminaes he proof of he exisence of a unique global soluion of.7.8 inx M. Now, we will prove he saemens a d. Le τ be a posiive real number saisfying we have u e Δ ϕ τ a C α +α r <τ< N α,.4 e sδ us τ ds+ b C e sδ vs τ ds. The smoohing properies of he hea semigroup.3, where p, q = r,τ on he firs and he second erm of he righ-hand side of he las inequaliy and wih j = of Corollary.5, give u e Δ ϕ τ a C + b C s N s N r τ r τ us r ds vs r ds. By using he inerpolaion inequaliy.8 wih s, r, τ =r,r,r,θ = θ,f = u on he firs erm of he righ-hand side of he las inequaliy and for he second erm we ake s, r, τ =r,s,s,θ = θ,f = v and he fac ha U and U belongs o X M, we obain he following esimaes u e Δ ϕ τ a CM s N + b CM s N r τ r τ s β ds s β ds.
16 A. Chouichi, S. Osmane and S. Tayachi NoDEA Thanks o he expressions of r and β given in Lemma.3 and due o.7, we deduce u e Δ ϕ τ CM a + b N τ α s N r τ s β ds..4 Using wih j = of Corollary.5 and he fac ha τ < r, he laer inequaliy gives u e Δ ϕ τ C N τ α,.4 where C is a finie posiive consan. On he oher hand, we se τ be a posiive real number saisfying α +α r <τ < N α..43 We aim o esimae v e Δ ϕ τ, wriing v e Δ ϕ τ c C e sδ usvs τ ds, hen, by using he smoohing effec, where p, q =τ,τ v e Δ ϕ τ c C s N τ τ usvs τ ds. Then, we apply Hölder inequaliy.5, for j =, we find v e Δ ϕ τ c C s N τ τ us r vs s ds. Thus, by he inerpolaion inequaliy.8, wih s, r, τ =r,r,r,θ = θ for f = u and for f = v, we ake s, r, τ =s,s,s,θ = θ, on he erm in he righ-hand side of he las inequaliy and he fac ha U and U belongs o X M, we obain v e Δ ϕ τ c CM s N τ τ s Γ ds..44 Thanks o he expressions of τ and Γ given in Lemma.3 and due o.7, we deduce v e Δ ϕ τ c CM N τ α s N τ τ s Γ ds..45 Using wih j = of Corollary.5 and he fac ha τ <s, he laer inequaliy gives v e Δ ϕ τ C N τ α,.46 where C is a finie posiive consan. Owing o he condiion.4 and.43, he righ-hand sides of.4 and.46 converge o zero as. This proves saemens a,b and d of Theorem.6. Also, i is clear ha.4 and.46 sill hold if τ = N α and τ = N α, his proves saemen c. Finally, we shall demonsrae.7. The proof of he L L esimaes is based on an ieraive argumen as in 8. Le us denoe he real numbers
17 Vol. 5 The complex valued nonlinear hea equaion r,r,s and s respecively by τ,τ,σ and σ. Choose real numbers τ,τ,σ and σ such ha, for j =,, we have +α j N +αj <τ <τ, <,.47 α j α j τ τ +α j N α j +α j <τ <τ, <,.48 α j α j τ τ and τ = α τ, σ = α α α τ, σ = α α τ..49 Remark ha a such choice is possible hanks o.3. We will concenrae firs on he equaion saisfied by v which is wrien as follows: v =e /Δ v/ + c / α j e sδ usvs ds. Therefore, he condiions.48, for j = and.49 allows us o use he smoohing effec of he hea semigroup.3, wih p, q =σ,σ onhe firs erm and p, q =τ,σ on he second erm of he righ-hand side of he inequaliy, and by applying Hölder inequaliy.5, for j =, we obain α N σ v σ C/ α N σ v/ σ + c C α N σ usvs τ ds, C/ α N σ v/ σ + c C α N σ vs s ds. / / s N s N τ σ τ σ us r Using he inerpolaion inequaliy.8, wih s, r, τ =r,τ,τ, θ = θ and s, r, τ =s,σ,σ, θ = θ respecively for f = u and f = v, and he fac ha U X M we obain α N σ v σ CD + c CD / s N τ σ s Γ ds,.5 where D = α N τ u τ, α N τ u τ, α N σ v σ, α N σ v σ > <..5 Wih he fac ha.48 is saisfied, for j =and.49, we deduce ha he inequaliy.5 leads o α N σ v σ CD <..5 >
18 A. Chouichi, S. Osmane and S. Tayachi NoDEA Now, we esimae α N σ v σ. Indeed, we have α N σ v σ C/ α N σ v/ σ + c C α N σ s N usvs τ ds C/ α N σ v/ σ + c C α N σ / / s N τ σ τ σ us r vs s ds, wherewehaveused.48, for j =,.49 and he smoohing effec of he hea semigroup.3, wih p, q =σ,σ on he firs erm and p, q =τ,σ on he second erm in he firs esimae and Hölder inequaliy.5, for j = in he las one. Now, applying he inerpolaion inequaliy.8, wih s, r, τ =r,τ, τ, θ = θ and s, r, τ =s,σ,σ, θ = θ respecively for f = u and f = v, and due o U X M, we obain α N σ v σ CD + c CD > / s N τ σ s Γ ds, where D is given in.5. By using.48, wih j =, he laer inequaliy leads o α N σ v σ CD <..53 Also, we wrie u =e /Δ u/ + a / e sδ u s ds + b / e sδ v s ds. Then, due o.47, for j = we use he smoohing properies of he hea semigroup.3 wih p, q {τ,τ, r,τ } o obain α N τ u τ C/ α N τ u/ τ + a C α N τ + b C α N τ / / s N s N r r τ us r ds τ vs r ds. Using he inerpolaion inequaliy.8 by aking s, r, τ =r,τ,τ, θ = θ for f = u and s, r, τ =r,σ,σ, θ = θ for f = v, we obain α N τ u τ CD + C a + b D / s N r where D is given in.5. Then, by.47, for j =,wehave > τ s β ds, α N τ u τ CD <..54
19 Vol. 5 The complex valued nonlinear hea equaion 3 Then, o esimae α N τ u τ, we use he smoohing properies of he hea semigroup.3 under he assumpion.47, for j = and.49, wih p, q, ϕ =τ,τ,u on he firs erm, p, q, ϕ = r,τ,u on he second erm and p, q, ϕ = r,τ,v on he hird erm, we obain α N τ u τ C/ α N τ u/ τ + a C α N τ / s N + b C α N τ s N / r τ r τ us r ds vs r ds. We consider s, r, τ =r,τ,τ, θ = θ and s, r, τ =r,σ,σ, θ = θ in he inerpolaion inequaliy.8 o apply i in he las inequaliy respecively for f = u and f = v and so, we obain α N τ u τ CD + C a + b D > / s N r τ s β ds, where D is given in.5. Then, by.47, for j =and.49, we have α N τ u τ CD <..55 The inequaliies.5,.53,.54 and.55 imply ha D = α N τ u τ, α N τ u τ, α N σ v σ, α N σ v σ > <. We ierae his procedure. For he nex sep, we consider τ,τ,σ and σ verifying, for j =, +α j N +αj <τ <τ, <,.56 α j α j τ τ +α j N α j +α j <τ <τ, <,.57 α j α j τ τ and τ = α τ, σ = α α α τ, σ = α α τ..58 Using similar esimaes as he previous sep wih he following inerpolaing numbers and r,j = θ j σ r,kj = θ kj τ + θ j σ ; α j + θ kj τ, k, j =,, s,j = θ j σ + θ j σ, j =,,
20 4 A. Chouichi, S. Osmane and S. Tayachi NoDEA wih θ kj and θ kj are as in Lemma.3 for k, j =, and τ,j = r,j + s,j. Remark ha we se r,j = r j and τ,j = r,j + s,j, where r,j = r j,s,j = s j,forj =, for he firs sep. We obain D = > α N τ u τ, α N τ u τ, α N σ u σ, α N σ u σ CM <. Therefore, we consruc he sequences {τ n } n which saisfies for j =, he following condiions +α j N +αj <τ n <τ n+, <, α j α j τ n τ n+ +α j N α j +α j <τ n <τ n+, α j α j α j <, τ n τ n+ for all ineger n. Then, we se he sequences {τ n} n, {σ n } n and {σ n} n such ha for all n =,,,... τ n = α τ n, σ n = α α α τ n, σ n = α α τ n,.59 One can check ha we can consruc a suiable sequence {τ n } n such ha i can reach, for some finie n, ha is τ n =, his prove.7, for r = s =. The inequaliy.7 follows by an argumen inerpolaion. The coninuous dependence inequaliy.8, for r, s =r,s ofhe soluion on he iniial daa resuls by considering F Φ U =U and F Φ U = U in he esimae.37. Formula.8, for r = s = can be proved saring wih.8, for r, s =r,s and using an ieraive procedure similar o he proof of.7, for r = s =. By Lemma of inerpolaion, we conclude.8. This achieves he proof of Theorem Self-similar soluions This secion is concerned wih he mild soluions of he sysem.9.3 which have a self-similar srucure wih power α, α. The inegral sysem relaed o.9.3 is given by w =e Δ ϕ + aμ w =e Δ ϕ + cμ e sδ w s ds + bν e sδ w s ds, 3. e sδ w sw s ds, 3. where a, b, c are he same parameers appearing in sysem.4 andμ, ν are given by.3. We firs esablish he global exisence only wih he norm N s. This is needed o prove he exisence of self-similar soluions in Theorem 3.3. In his secion, we will use α and α saisfying., r saisfying.3 and s be given by.4, β and γ be given by.7.
21 Vol. 5 The complex valued nonlinear hea equaion 5 For Φ = ϕ,ϕ S R N S R N, we define N s by N s Φ := β e Δ ϕ r, γ e Δ ϕ s. 3.3 > For <δ<δ, where δ is given by δ = N +α max, +α maxα,α r α α, 3.4 we define N δ by N δ Φ := β +δ e Δ ϕ r, γ+δ e Δ ϕ s. 3.5 > We firs give examples of homogeneous iniial values wih finie norm N defined by.6. We firs recall he following resul due o,8. Proposiion 3..,8 Le N be an ineger. Le α, α be wo real numbers such ha N α α, >. α Le r,r be wo real numbers such ha Le r = α α r, r > N α. β = α N r, β = α N r. Le x ϕx =ω x α, x where ω L r S N. Then, for any cu-off funcion η saisfying η near he origin and having a compac por, 3.6 we have he following: i > β e Δ ϕ r <, ii > β+δ e Δ ηϕ r <, for <δ< N α, iii > β e Δ ηϕ r < ; iv > β e Δ ηϕ r <. Also, we give examples of iniial values wih finie norm N s given by 3.3. These iniial values are used in Theorems 3.3 and 4. below. Proposiion 3.. 6, Proposiion.3 Le N be an ineger. Le α,α be posiive real numbers which saisfy.. Leα,α be posiive real numbers which saisfy.5. Suppose ha N N >, >. α α
22 6 A. Chouichi, S. Osmane and S. Tayachi NoDEA Le r be a real number saisfying.3 and r,s and s be given by.4. Le β,γ and β,γ be given by.7 and.8 respecively. Le ϕ and ψ be wo empered disribuions homogeneous of degree α, α respecively. If ϕx =ω x x α and ψx =ω x x α, 3.7 where ω L r S N and ω L s S N are homogeneous of degree, hen, N s ϕ, ψ <, 3.8 where N s is given by 3.3. Also, for any cu-off funcion η saisfying η near he origin and having a compac por, 3.9 we have he following: i > β+δ e Δ ηϕ r <, for <δ< N α ; > γ+δ e Δ ηψ s <, for <δ< N α ; ii > β e Δ ηϕ r < ; > γ e Δ ηψ s < ; iii N ηϕ, ηψ <, wheren is given by.6. We esablish he global exisence wih he norm N s which is given by 3.3 and wih he norm N δ is given by 3.5. This is needed o prove he exisence of self-similar soluions. Theorem 3.3. Le N be an ineger. Le α and α be posiive real numbers saisfying.. Suppose ha N N > and α α >. Le r be a real number saisfying.3 and s be given in.4. Leβ and γ be given by.7 and define β r and γ s by β r =α N r, r r,, 3. γ s =α N s, s s,. 3. Le M > be such ha C := CM <, where C is given by 3.3 and 3.34 below. Choose R > such ha R + CM M. If Φ = ϕ,ϕ S R N S R N such ha N s Φ R, 3. where N s is given by 3.3, hen, he inegral sysem has a unique global soluion W =w,w such ha > βr w r, γs w s M, r r,, s s,. 3.3 In addiion, if W =w,w and W = w, w respecively are he soluions of he sysem wih iniial values Φ=ϕ,ϕ and Ψ=ψ,ψ which saisfy 3., hen, we have > β w w r, γ w w s C N s Φ Ψ, 3.4
23 Vol. 5 The complex valued nonlinear hea equaion 7 where N s is given by 3.3. Also, for some <δ<δ, where δ is given by 3.4, we have β +δ w w r, γ+δ w w s > C δ N δ Φ Ψ, 3.5 where N δ is given by 3.5, C δ is given by 3.8 and 3.36 below. The posiive consan M is chosen small enough so ha C δ <. Furhermore, If Φ=ϕ,ϕ and ϕ,ϕ be as in he Proposiion 3., hen, he resuling soluion of wih iniial daa Φ is self-similar, denoe i by W =w,w. LeW =w,w be he soluion of wih iniial daa ηφ, η is a cu-off funcion saisfying 3.9. Then,we have w w r C δ βr δ, >, r r,, 3.6 w w s C δ γs δ, >, s s,. 3.7 The real number M is smaller. A his sage, we conclude ha he soluion W is asympoically self-similar in he L L -norm. Remark The saemens a d of Theorem.6 are also saisfied by global soluion W =w,w given by Theorem The soluion W given by Theorem 3.3 saisfy W, x =w, x, w, x = α w,x/, α w,x/. 3.8 By using he simple dilaaion argumen, he resuls is given as follow: α w,. w,. r C δ δ, >, r r,, 3.9 α w,. w,. C δ δ, >, s s,. 3. s Proof of Theorem 3.3 Le X be he se of Bochner measurable funcions: W :. L r R N L s R N W :=w,w such ha W X := β w r, γ w s <, 3. > where r is a real number saisfying.3, s is given by.4, β and γ are given by.7. Le M be a posiive real number. Define X M = {W X, W X M}. In his proof, we do no need o rea all he cases described by μ and ν. In fac, i if μ = ν =, hen he asympoic sysem is he linear hea sysem: w =Δw, w =Δw. This case can be reaed as in 6, ii if μ = ν =, hen he asympoic sysem is he nonlinear hea sysem.7.8. This case is sudied in 8.
24 8 A. Chouichi, S. Osmane and S. Tayachi NoDEA So, we are ineresed only by he cases μ =,ν=andμ =,ν=. Case : μ =and ν =. We have, by Lemma.3, r = r,β = β, τ = r + s and Γ = β + γ. Le us consider he mapping FΦ s defined by F Φ s W =F Φ sw,gs Φ W, where W =w,w X M, Φ=ϕ,ϕ S R N S R N and F s Φ W =eδ ϕ + a G s Φ W =eδ ϕ + c e sδ w s ds, e sδ w sw s ds. Through calculaions similar o he proof of Theorem.6, wehaveforw, W X M FΦW s FΦ s W XM N s Φ Ψ + C W W XM, 3. where N s is defined by 3.3, C is a finie posiive consan given by such ha C =M a C C =M c C C = maxc,c, 3.3 σ N r σ β dσ, 3.4 σ N r σ γ β dσ. 3.5 So, he mapping FΦ s has a unique fixed poin in X M and 3.4 follows similarly as in he proof of Theorem.6. Now,leΦ, Ψ, W =w,w and W = w, w. We esimae he difference W W wih he norm W X,δ := β +δ w r, γ+δ w s <, 3.6 > o obain > wih where β +δ w w r, γ+δ w w s Cδ N δ Φ Ψ, C δ =M a C C δ =M c C 3.7 C δ = maxc δ,c δ, 3.8 σ N r σ β δ dσ, σ N r σ γ β δ dσ. Since <δ<δ, where δ is given by 3.4 one can see ha β + δ <,β + γ + δ<andc δ is a finie posiive consan. This proves 3.5.
25 Vol. 5 The complex valued nonlinear hea equaion 9 Le Φ = ϕ,ϕ be as in Proposiion 3. andψ= ηφ. I follows from formula 3.5, ha β +δ w w r, γ+δ w w s CNδ Φ ηφ > = CN δ η Φ. 3.9 Using par i of Proposiion 3., we have ha N δ η Φ <, for<δ<δ. Thus, we ge 3.6 and 3.7, for r, s =r,s. The L L asympoic self-similar esimaes: Here we wrie w w =e Δ w / w / +c e sδ w sw s w sw s ds, hus, by he smoohing properies of he hea semigroup.3, for p, q = s, andϕ = w / w /, we obain α +δ w w C / α +δ N s w / w / s + c C α +δ Now, we compue ha, for arbirary T> / w sw s w sw s ds. α +δ w w C / γ+δ w / w / s + MC c α+ s α α δ ds / α+δ w w,,t α +δ w w, where M is as in Theorem.6. By3.7, for s = s and he fac ha α =, he las inequaliy becomes α +δ w w C δ + c CM,δ α+δ w,t,t Similarly, we wrie w w =e Δ w / w / + a w, α +δ w w. 3.3 e sδ w s w s ds.
26 3 A. Chouichi, S. Osmane and S. Tayachi NoDEA Thus, by he smoohing properies of he hea semigroup.3, for p, q = r, andϕ = w w, for arbirary T>and < T, we compue ha α+δ w w C / α+δ N r w / w / r +M C a α+ s α δ ds / α+δ w w,,t where M is as in Theorem.6. By3.6, for r = r and he fac ha α =, he las inequaliy becomes α+δ w w,t C δ + a CM,δ α+δ w w, α +δ,t w w. 3.3 Since CM,δ ifm, i is clear ha if M is sufficienly small hen 3.3 and 3.3 imply ha α+δ w w, α +δ w w C δ. 3.3,T Since he las consan C δ does no depend on he arbirary real number T>, he esimaes 3.6 and 3.7, for r = s = are valid for all >. The general case for 3.6 and 3.7 follows by inerpolaion. Case : μ =and ν =. We have, by Lemma.3, r = s and β = γ. Le us consider he mapping FΦ s defined by F Φ s W =F Φ sw,gs Φ W, where W =w,w X M, Φ= ϕ,ϕ S R N S R N and F s Φ W =eδ ϕ + b e sδ w s ds, G s Φ W =eδ ϕ. Through calculaions similar o he proof of Theorem.6, wehaveforw, W X M F s ΦW FΦ s W N s Φ Ψ + C W W XM, 3.33 XM where N s is defined by 3.3, C is a finie posiive consan given by C =M b C σ N s r σ γ dσ We conclude ha he mapping F s Φ has a unique fixed poin in X M and 3.4 follows as in Theorem.6.
27 Vol. 5 The complex valued nonlinear hea equaion 3 Similarly, We esimae he difference W W wih he norm defined by 3.6 andweseφ, Ψ, W=w,w and W = w, w. We find β +δ w w r, γ+δ w w s Cδ N δ Φ Ψ, > wih C δ =M b C σ N s 3.35 r σ γ δ dσ Since <δ<δ, where δ is given by 3.4, noe ha γ + δ<, C δ is a finie posiive consan and 3.5 follows. Le Φ = ϕ,ϕ be as in Proposiion 3. andψ= ηφ. I follows from he formula 3.5, ha > β +δ w w r, γ+δ w w s CNδ Φ ηφ = CN δ η Φ Using par i of Proposiion 3., we have ha N δ η Φ <, for<δ<δ. Thus, we obain 3.6 and 3.7, for r, s =r,s. The L L -asympoic self-similar esimaes: here we wrie w w =e Δ w / w /. We compue, by he smoohing properies of he hea semigroup.3 and 3.7 fors = s α +δ w w C / γ+δ w / w / s C δ Now, we esimae α+δ w w. We have w w =e Δ w / w / + b e sδ w s w s ds. Thus, by he smoohing properies of he hea semigroup.3, for p, q = r, on he second and he hird erm of he righ-hand side of he las inequaliy, for arbirary T> and < T, we compue ha α+δ w w C / α+δ N r w / w / r +M C b α α + s α δ ds / α +δ w w, 3.39,T where M is as in Theorem.6. By3.6, for r = r, and he fac ha α = α +, he las inequaliy becomes
28 3 A. Chouichi, S. Osmane and S. Tayachi NoDEA α+δ w w C δ + b CM,δ,T α+δ w w, α +δ,t w w. 3.4 Since CM,δ ifm, i is clear ha if M is sufficienly small hen 3.38 and 3.4 imply ha α+δ w w, α +δ w w C δ. 3.4,T Since he las consan C δ does no depend on he arbirary real number T>, he esimaes 3.6 and 3.7 forr = s = are valid for all >. The general case for 3.6 and 3.7 will be deduced from inerpolaion. ProofofTheorem. Le u,v be as in he assumpions of he Theorem.. Then, by Par i of Proposiion 3., we have N u,v <. Le ε> be such ha max c, c <εand u,v saisfies.5. Then, by Theorem.6, here exiss u, v global mild soluion of.4. Since u,v L R N CR N, hen, u, v is he soluion of.4 and is global. Proof of Theorem. Le u,v be as in he assumpions of he Theorem.. Then by 3.8, we have N u,v <. Leε> be such ha max c, c <εand u,v saisfies 3.. Then by Theorem 3.3, here exiss w,w global mild soluion of.. Since u,v L R N CR N, hen, w,w is he soluion of. and is global. Using he Theorem 3.3, we conclude ha he resuling soluion w,w is self-similar. 4. Asympoically self-similar soluions In his secion, we are mainly concerned wih he proof of he asympoic behavior resuls for some global soluions of he sysem.7.8 wih small iniial daa wih respec o he norm N. These allowed iniial daa ϕ,ϕ decrease in space as x α, x α, where α,α are any real numbers such ha hey saisfy. andα,α < N. We fulfil he proof of Theorem 3.3 hrough he following lemma. Lemma 4.. Le N be an ineger. Le α,α and α,α be posiive real numbers which saisfy respecively. and.5. Suppose ha N N >, α α >. Le r j,s j,β j and γ j,forj =, be as in Lemma.. Leμ, ν be given by.3 and δ>. Ler and β be as in Lemma.3 given also by.. We define he inerpolaing numbers r and β as follow: = μδ +, β = β + r +α r μδ +α.
29 Vol. 5 The complex valued nonlinear hea equaion 33 Moreover, by he formula. of r and β, we se he inerpolaing numbers s and γ which be wrien as follow: s = νδ +, γ νδ = β +. r +α +α Furhermore, from he numbers τ and Γ cied in Lemma., we inroduce he inerpolaing numbers τ and Γ as follow: τ = μδ +, τ +α Γ μδ =Γ + +α. Also, here exiss r r,r,s s,s,β β,β and γ γ,γ such ha = +, Γ = β + γ. 4. τ r s Then, here exiss a real number δ >, which can be compued, such ha for all <δ<δ he numbers defined recenly verify he following assumpions: i There exiss ζ kj,ζ kj, fork, j {,,, } such ha and r kj = ζ kj r + ζ kj r, s kj = ζ kj s + ζ kj s, β = ζ β + ζ β, γ = ζ γ + ζ γ, β = ζ β + ζ β, γ = ζ γ + ζ γ, ii < r <r, < s <r, <τ <s, iii β + μδ <, γ + νδ <, Γ + μδ <, iv N r N r <, s N r <, τ s <, v + β N r r β + μδ =, +β N s r γ + νδ =, +γ N τ s Γ + μδ =. Proof. Owing o he condiions saisfied by r,r,s,s,β,β,γ and γ in he Lemmas. and.3 and in he Corollary.5, he proof of Lemma 4. is simple and can be omied. Theorem 4.. Le N be an ineger. Le α,α,α and α be posiive real numbers which saisfy α, α α + α, α α +. Suppose ha N N > and α α >. Le r be a real number saisfying.3 and s defined in.4. Leβ and γ be given by.7. LeΦ and η be as in Proposiion 3.. Assume ha.3.4 are saisfied.
30 34 A. Chouichi, S. Osmane and S. Tayachi NoDEA Le W given by 3.8 be he self-similar soluion of.9.3 wih iniial daa Φ given by Theorem 3.3 and le U be he global soluion of.7.8 wih iniial daa ηφ consruced by Theorem.6 we muliply Φ by a small consan so ha.5 and hen 3. are saisfied wih boh Φ and ηφ. Then, here exiss a real number δ >, which can be compued, such ha for all δ saisfying <δ<δ here exiss a posiive consan C δ such ha for r r,,s s,, u w r C δ βr δ, >, 4. v w s C δ γs δ, >, 4.3 where β r and γ s are given respecively by 3. and 3.. Hence U =u, v is asympoically self-similar in he L L -norm. Furhermore, here exiss wo posiive consans d and d such ha, for large ime, we have d α u d α, d α v d α. 4.4 We require ha he real number M appearing in Theorem.6 mus be smaller so ha C δ < where C δ is given by 3.8 and Remark 4.3. Remark ha, by he dilaaion argumen, we can prove he following inequaliies: α u,. w,. r C δ δ, >, r r,, 4.5 α v,. w,. C δ δ, >, s s,. 4.6 s Proof. Over he proof, we use he noaions esablished in Lemma 4.. The sysem.7.8 coincides wih he sysem in he paricular case where μ = ν =. As well as he esimaes 4. and 4.3 follow from hose esablished in he Theorem 3.3. We prove he resuls of Theorem 4. only for wo cases μ =,ν=andμ =,ν=, since he cases μ = ν = and μ = ν = are reaed as well as in 6,8 respecively. Case : μ =and ν =. Sep : L r L s -asympoic resuls. LeΨ=ψ,ψ S R N S R N saisfying he condiion.5. Le U =u, v be he soluion of.7.8 wih iniial daa Ψ consruced by Theorem.6. LeW =w,w behe soluion of he sysem: w =e Δ ψ + a w =e Δ ψ + c which given by Theorem 3.3. We have u w r a + b e sδ w s ds, 4.7 e sδ w sw s ds, 4.8 e sδ u s w s r ds e sδ v s r ds, 4.9
31 Vol. 5 The complex valued nonlinear hea equaion 35 v w s c e sδ usvs w sw s s ds. 4. Le δ be such ha <δ<δ, where δ is a small posiive real number. We firs deal wih he inequaliy 4.. By Lemma 4. and he smoohing properies of he hea semigroup.3 wih p, q =τ,s andϕ = usvs w sw s, we have v w s C c s N τ s usvs w sw s τ ds, 4. where τ is given in Lemma.3. In fac, since μ =wehaveα =andwe wrie τ = +α r = r + s.so,byhölder inequaliy, we ge uv w w τ v s u w r + w r v w s. 4. Le T be an arbirary posiive number. Injecing 4. in4., we obain, for < T where γ+δ v w s,t C δ γ+δ N r β γ δ+ β+δ u w r, γ+δ v w s, C δ =CM c s N r s β γ δ ds, he posiive consans C δ is finie. Noe ha, in his case we have α =,so Then, we obain γ+δ v w s C δ γ + δ N r β γ δ +=.,T β+δ u w r, γ+δ v w s. 4.3 Now we esimae he inequaliy 4.9. By Lemma 4. and he smoohing properies of he hea semigroup.3 wih p, q, ϕ = r,r,u w on he firs erm and wih p, q, ϕ = s,r,v on he second erm of he righ-hand side of he inequaliy 4.9, we have u w r C a +C b s N s N r r u s w s r/ ds s r v s s / ds. 4.4 Le T > be an arbirary real number. Using Lemma 4., Eq..8 wih s, r, τ, θ =s,s,s,ζ on he second erm of he righ-hand side of he las inequaliy, we ge, for < T β+δ u w r C δ β +δ u w r + Cδ,,T
32 36 A. Chouichi, S. Osmane and S. Tayachi NoDEA where C δ =MC a C δ = M C b s N r s β δ ds, s N s r s γ ds. By Lemma 4., we find ha he posiive consans C δ,c δ are finie. Thus, we obain β+δ u w r C δ C δ, 4.5 for a given consan C δ, since i does no depend on T he pervious inequaliies hold on he whole inerval,. I follows ha, for all δ saisfying, <δ<δ, here exiss a posiive consan C δ, such ha u w r C δ β δ, >, 4.6 v w s C δ γ δ, >. 4.7 Sep : L L -asympoic resul. Le Φ = ϕ,ϕ be as in Proposiion 3., hen using he resuls , for r, s =r,s of Theorem 3.3, one obains ha, for all <δ<δ, here exiss a posiive consan C δ >, such ha w w r C δ β δ, >, 4.8 w w s C δ γ δ, >, 4.9 where δ is given by 3.4. Hence, W =w,w is soluion of wih iniial daa ηφ, where η is a cu-off funcion saisfying 3.9. Then by Proposiion 3. iii we have ha N ηφ is finie. Thus, he inequaliies 4. and 4.3 follow by wriing U W = U W + W W and using Le δ> be sufficienly small and recall he following numbers given in i of Lemma 4., ζ = θ ; ζ = θ + δ α α. 4. In paricular, δ is chosen small enough so ha ζ and ζ belong o, and <δ<δ. Wrie now v w =e Δ v/ w / +c e sδ usvs w sw s ds. Then, by.3, 4. and 4.7, we have v w e Δ v/ w / + c e sδ usvs w sw s ds.
33 Vol. 5 The complex valued nonlinear hea equaion 37 Tha is α +δ v w C / γ+δ v/ w / s + c C α +δ usvs w sw s ds C δ + C c α +δ / + w s vs w s ds. Using.7, we ge for arbirary T>, we obain α +δ v w C δ + CM α +δ,t vs us w s / s α α δ ds α+δ u w, α +δ v w C δ + CM α +δ α α δ+ / s α α δ ds α+δ u w, α +δ v w.,t Thus, we obain, from α =, ha α +δ v w C δ +CM,δ α+δ u w, α +δ v w. 4.,T Le us wrie now u w =e Δ u/ w / + a +b e sδ v s ds. e sδ u s w s ds We have α+δ u w α+δ e Δ u/ w / + a α+δ e sδ u s ws ds + b α+δ e sδ v s ds. Therefore by.3 and 4.6, we obain α+δ u w C / β+δ u/ w / r + C a α+δ / u s w s ds
34 38 A. Chouichi, S. Osmane and S. Tayachi NoDEA +C b α+δ / v s ds C δ + C a α+δ us + w s / us w s ds +C b α+δ vs ds. Due o.7, and an inerpolaion argumen, we ge for arbirary T>, α+δ u w C δ +MC a α+δ s α ζ + ζ α δ ds Hence,,T / / αζ+ ζα+δ u w +CM b α+δ α s ζ + ζ α / ds. α+δ u w C δ +MC a +α αζ ζα s α ζ + ζ α δ ds / αζ+ ζα+δ u w,t +M C b +α α ζ + ζ α +δ ds. α s ζ + ζ α / From he expressions of ζ,ζ given by 4., we obain α+δ u w C δ + CM,δ+CM αζ+ ζα+δ u w. 4.,T We subsiue ζ = θ = and obain αζ+ ζα+δ u w = α+δ u w.,t,t 4.3 Case : μ =and ν =. Sep : L r L s -asympoic resuls. LeΨ=ψ,ψ S R N S R N saisfying he condiion.5. Le U =u, v be he soluion of.7.8 wih iniial daa Ψ consruced by Theorem.6. LeW =w,w behe
35 Vol. 5 The complex valued nonlinear hea equaion 39 soluion of he sysem: w =e Δ ψ + b e sδ w s ds, 4.4 w =e Δ ψ, 4.5 which is given by Theorem 3.3. Wehave u w r b + a v w s c e sδ v s w s r ds e sδ u s r ds, 4.6 e sδ usvs s ds. 4.7 Le δ be such ha <δ<δ, where δ is a small posiive real number. We firs deal wih he inequaliy 4.7. By Lemma 4. and he smoohing properies of he hea semigroup.3 wih p, q =τ,s andϕ = usvs, we have v w s C c s N τ s usvs τ ds. 4.8 where τ is given by 4.. Using 4., Hölder inequaliy, we ge uv τ v s u r. 4.9 Le T be an arbirary posiive number. Injecing 4.9 in4.8 and applying.8 wih s, r, τ, θ = r,r,r,ζ for f = u and s, r, τ, θ = s,s,s,ζ forf = v and using Lemma 4., we obain, for < T where C δ = CM c γ+δ v w s C δ, 4.3 s N τ s s Γ ds. By pars iii, iv of Lemma 4. and by he fac <δ<δ, he posiive consans C δ is finie. Now we esimae he inequaliy 4.6. By Lemma 4. and he smoohing properies of he hea semigroup.3 wih p, q, ϕ = s,r,v wand p, q, ϕ = r,r,u respecively on he firs and he second erm of he righ-hand side of he inequaliy 4.6, we have u w r C a s N r r u s r / ds +C b s N s r v s ws s/ ds. 4.3 Le T > be an arbirary real number. Using Lemma 4., Eq..8 wih s, r, τ, θ =r,r,r,ζ on he firs erm of he righ-hand side of he las
36 4 A. Chouichi, S. Osmane and S. Tayachi NoDEA inequaliy, we ge, for < T β+δ u w r C δ + C δ β+δ v w s, where C δ = M C a s N r r s β ds, C δ =MC b s N s s γ δ ds. By Lemma 4., we find ha he posiive consans C δ,c δ are finie. Thus, we obain for a given consan C δ, since i does no depend on T he pervious inequaliies hold on he whole inerval,. I follows ha, for all δ saisfying, <δ<δ, here exiss a posiive consan C δ, such ha 4.6 and 4.7 hold. Sep : L L -asympoic resul. Le Φ = ϕ,ϕ be as in Proposiion 3., hen using he inequaliies , for r, s =r,s of Theorem 3.3, one obains ha, for all <δ<δ, here exiss a posiive consan C δ >, such ha 4.8 and 4.9 hold. Hence, W =w,w is soluion of wih iniial daa ηφ, where η is a cu-off funcion saisfying 3.9. Then, by Proposiion 3. iii, we have ha N ηφ is finie. Thus, he inequaliies 4. and 4.3 follow by wriing U W = U W + W W and using Le δ> be sufficienly small and recall he following numbers given in i of Lemma 4., ζ = θ + δ α α ; ζ = θ, 4.3 ζ α α +ζ α α =θ α α +θ α α +δ In paricular, δ is chosen small enough so ha ζ,ζ,ζ and ζ belong o, and <δ<δ. Wrie now v w =e Δ v/ w / + c e sδ usvs ds. We have α +δ v w α +δ e Δ v/ w / + c α +δ e sδ usvs ds. Tha is, hen by.3 we obain α +δ v w C / γ+δ v/ w / s + c C α +δ us vs ds. Using.7, 4.7 and an inerpolaion argumen, we ge for arbirary T>, we obain
37 Vol. 5 The complex valued nonlinear hea equaion 4 α +δ v w C δ + C c M α +δ α s ζ + ζ α +α ζ + ζ α / C δ + C c M +α αζ+ ζα+α ζ + ζ α δ ds. α s ζ + ζ α +α ζ + ζ α / ds Now hanks o he relaion beween ζ and ζ given by 4.33, we obain Le us wrie now We have α +δ v w C δ + C c M u w =e Δ u/ w / + a +b e sδ v s w s ds. e sδ u s ds α+δ u w α+δ e Δ u/ w / + a + b Therefore by.3 and 4.6, we obain e sδ u s ds e sδ v s w s ds. α+δ u w C / β+δ u/ w / r +C a α+δ u s ds / +C b α+δ / v s w s ds C δ + C a α+δ us ds / +C b α+δ vs + w s / vs w s ds. Due o.7 and an inerpolaion argumen, we ge for arbirary T>, α+δ u w C δ + C α+δ M a s / α ζ + ζ α ds
Asymptotic analysis of a non-linear non-local integro-differential equation arising from bosonic quantum field dynamics
 Nonlinear Differ. Equ. Appl. 21 (214), 51 61 c 213 Springer Basel 121-9722/14/151-11 published online May 8, 213 DOI 1.17/s3-13-237-y Nonlinear Differenial Equaions and Applicaions NoDEA Asympoic analysis
Nonlinear Differ. Equ. Appl. 21 (214), 51 61 c 213 Springer Basel 121-9722/14/151-11 published online May 8, 213 DOI 1.17/s3-13-237-y Nonlinear Differenial Equaions and Applicaions NoDEA Asympoic analysis
The LWR Model in Lagrangian coordinates
 The LWR Model in Lagrangian coordinaes ACI-NIM: Mah Models on Traffic Flow Ludovic Leclercq, LICIT (ENTPE/INRETS) Jorge Laval, Georgiaech Universiy 31 ocober 2007 INRETS Ouline Lagrangian resoluion of
The LWR Model in Lagrangian coordinaes ACI-NIM: Mah Models on Traffic Flow Ludovic Leclercq, LICIT (ENTPE/INRETS) Jorge Laval, Georgiaech Universiy 31 ocober 2007 INRETS Ouline Lagrangian resoluion of
Exercise 6.14 Linearly independent vectors are also affinely independent.
 Affine sets Linear Inequality Systems Definition 6.12 The vectors v 1, v 2,..., v k are affinely independent if v 2 v 1,..., v k v 1 is linearly independent; affinely dependent, otherwise. We first check
Affine sets Linear Inequality Systems Definition 6.12 The vectors v 1, v 2,..., v k are affinely independent if v 2 v 1,..., v k v 1 is linearly independent; affinely dependent, otherwise. We first check
Basic statistics for experimental medical researchers
 Basic statistics for experimental medical researchers Sample size calculations September 15th 2016 Christian Pipper Department of public health (IFSV) Faculty of Health and Medicinal Science (SUND) E-mail:
Basic statistics for experimental medical researchers Sample size calculations September 15th 2016 Christian Pipper Department of public health (IFSV) Faculty of Health and Medicinal Science (SUND) E-mail:
Deepak Kumar Dubey, V. K. Jain RATE OF APPROXIMATION FOR INTEGRATED SZASZ-MIRAKYAN OPERATORS
 DEMONSTRATIO MATHEMATICA Vol. XLI No 4 8 Deepak Kumar Dubey, V. K. Jai RATE OF APPROXIMATION FOR INTEGRATED SZASZ-MIRAKYAN OPERATORS Absrac. Recely Jai e al. [3] proposed a iegral modificaio of Szasz-Mirakya
DEMONSTRATIO MATHEMATICA Vol. XLI No 4 8 Deepak Kumar Dubey, V. K. Jai RATE OF APPROXIMATION FOR INTEGRATED SZASZ-MIRAKYAN OPERATORS Absrac. Recely Jai e al. [3] proposed a iegral modificaio of Szasz-Mirakya
AALBORG UNIVERSITY. Spectral Analysis of a δ-interaction in One Dimension Defined as a Quadratic Form
 AALBOG UNIVESITY Specral Analysis of a δ-ineracion in One Dimension Defined as a Quadraic Form by Peer Jensen February 9h, 008 Maser Thesis Deparmen of Mahemaical Sciences Aalborg Universiy Fredrik Bajers
AALBOG UNIVESITY Specral Analysis of a δ-ineracion in One Dimension Defined as a Quadraic Form by Peer Jensen February 9h, 008 Maser Thesis Deparmen of Mahemaical Sciences Aalborg Universiy Fredrik Bajers
Critical exponent for semilinear wave equation with critical potential
 Nonlinear Differ. Equ. Appl. (13), 1379 1391 c 1 Springer Basel 11-97/13/31379-13 published online December 16, 1 DOI 1.17/s3-1-14-x Nonlinear Differential Equations and Applications NoDEA Critical exponent
Nonlinear Differ. Equ. Appl. (13), 1379 1391 c 1 Springer Basel 11-97/13/31379-13 published online December 16, 1 DOI 1.17/s3-1-14-x Nonlinear Differential Equations and Applications NoDEA Critical exponent
DoodleBUGS (Hands-on)
 DoodleBUGS (Hands-on) Simple example: Program: bino_ave_sim_doodle.odc A simulation example Generate a sample from F=(r1+r2)/2 where r1~bin(0.5,200) and r2~bin(0.25,100) Note that E(F)=(100+25)/2=62.5
DoodleBUGS (Hands-on) Simple example: Program: bino_ave_sim_doodle.odc A simulation example Generate a sample from F=(r1+r2)/2 where r1~bin(0.5,200) and r2~bin(0.25,100) Note that E(F)=(100+25)/2=62.5
Sign variation, the Grassmannian, and total positivity
 Sign variation, the Grassmannian, and total positivity arxiv:1503.05622 Slides available at math.berkeley.edu/~skarp Steven N. Karp, UC Berkeley FPSAC 2015 KAIST, Daejeon Steven N. Karp (UC Berkeley) Sign
Sign variation, the Grassmannian, and total positivity arxiv:1503.05622 Slides available at math.berkeley.edu/~skarp Steven N. Karp, UC Berkeley FPSAC 2015 KAIST, Daejeon Steven N. Karp (UC Berkeley) Sign
Multivariate Extremes and Dependence in Elliptical Distributions
 Multivariate Extremes and Dependence in Elliptical Distributions Filip Lindskog, RiskLab, ETH Zürich joint work with Henrik Hult, KTH Stockholm I II III IV V Motivation Elliptical distributions A class
Multivariate Extremes and Dependence in Elliptical Distributions Filip Lindskog, RiskLab, ETH Zürich joint work with Henrik Hult, KTH Stockholm I II III IV V Motivation Elliptical distributions A class
x t X t, t 1 τ =0 A t,τ (ξ t )x t τ = h t (ξ t )
 POLYHEDRAL RISK MEASURES IN SOCHASIC PROGRAMMING A. EICHHORN AND W. RÖMISCH Absrac. Sochasic programs ha do no only minimize expeced cos bu also ake ino accoun risk are of grea ineres in many applicaion
POLYHEDRAL RISK MEASURES IN SOCHASIC PROGRAMMING A. EICHHORN AND W. RÖMISCH Absrac. Sochasic programs ha do no only minimize expeced cos bu also ake ino accoun risk are of grea ineres in many applicaion
PARALLELIZATION OF ATTILA SIMULATOR WITH OPENMP MIGUEL ÁNGEL MARTÍNEZ DEL AMOR MINIPROJECT OF TDT24 NTNU
 PARALLELIZATION OF ATTILA SIMULATOR WITH OPENMP MIGUEL ÁNGEL MARTÍNEZ DEL AMOR MINIPROJECT OF TDT24 NTNU OUTLINE INEFFICIENCY OF ATTILA WAYS TO PARALLELIZE LOW COMPATIBILITY IN THE COMPILATION A SOLUTION
PARALLELIZATION OF ATTILA SIMULATOR WITH OPENMP MIGUEL ÁNGEL MARTÍNEZ DEL AMOR MINIPROJECT OF TDT24 NTNU OUTLINE INEFFICIENCY OF ATTILA WAYS TO PARALLELIZE LOW COMPATIBILITY IN THE COMPILATION A SOLUTION
Generalized Probit Model in Design of Dose Finding Experiments. Yuehui Wu Valerii V. Fedorov RSU, GlaxoSmithKline, US
 Generalized Probit Model in Design of Dose Finding Experiments Yuehui Wu Valerii V. Fedorov RSU, GlaxoSmithKline, US Outline Motivation Generalized probit model Utility function Locally optimal designs
Generalized Probit Model in Design of Dose Finding Experiments Yuehui Wu Valerii V. Fedorov RSU, GlaxoSmithKline, US Outline Motivation Generalized probit model Utility function Locally optimal designs
Besvarelser til Lineær Algebra Reeksamen Februar 2017
 Besvarelser til Lineær Algebra Reeksamen - 7. Februar 207 Mikkel Findinge Bemærk, at der kan være sneget sig fejl ind. Kontakt mig endelig, hvis du skulle falde over en sådan. Dette dokument har udelukkende
Besvarelser til Lineær Algebra Reeksamen - 7. Februar 207 Mikkel Findinge Bemærk, at der kan være sneget sig fejl ind. Kontakt mig endelig, hvis du skulle falde over en sådan. Dette dokument har udelukkende
SKRIFTLIG EKSAMEN I NUMERISK DYNAMIK Bygge- og Anlægskonstruktion, 7. semester Torsdag den 19. juni 2003 kl Alle hjælpemidler er tilladt
 SKRIFTLIG EKSAMEN I NUMERISK DYNAMIK Bygge- og Anlægskonstruktion, 7. semester Torsdag den 9. juni 23 kl. 9.-3. Alle hjælpemidler er tilladt OPGAVE f(x) x Givet funktionen f(x) x, x [, ] Spørgsmål (%)
SKRIFTLIG EKSAMEN I NUMERISK DYNAMIK Bygge- og Anlægskonstruktion, 7. semester Torsdag den 9. juni 23 kl. 9.-3. Alle hjælpemidler er tilladt OPGAVE f(x) x Givet funktionen f(x) x, x [, ] Spørgsmål (%)
University of Copenhagen Faculty of Science Written Exam April Algebra 3
 University of Copenhagen Faculty of Science Written Exam - 16. April 2010 Algebra This exam contains 5 exercises which are to be solved in hours. The exercises are posed in an English and in a Danish version.
University of Copenhagen Faculty of Science Written Exam - 16. April 2010 Algebra This exam contains 5 exercises which are to be solved in hours. The exercises are posed in an English and in a Danish version.
On the complexity of drawing trees nicely: corrigendum
 Acta Informatica 40, 603 607 (2004) Digital Object Identifier (DOI) 10.1007/s00236-004-0138-y On the complexity of drawing trees nicely: corrigendum Thorsten Akkerman, Christoph Buchheim, Michael Jünger,
Acta Informatica 40, 603 607 (2004) Digital Object Identifier (DOI) 10.1007/s00236-004-0138-y On the complexity of drawing trees nicely: corrigendum Thorsten Akkerman, Christoph Buchheim, Michael Jünger,
Probabilistic properties of modular addition. Victoria Vysotskaya
 Probabilistic properties of modular addition Victoria Vysotskaya JSC InfoTeCS, NPK Kryptonite CTCrypt 19 / June 4, 2019 vysotskaya.victory@gmail.com Victoria Vysotskaya (Infotecs, Kryptonite) Probabilistic
Probabilistic properties of modular addition Victoria Vysotskaya JSC InfoTeCS, NPK Kryptonite CTCrypt 19 / June 4, 2019 vysotskaya.victory@gmail.com Victoria Vysotskaya (Infotecs, Kryptonite) Probabilistic
Aktivering af Survey funktionalitet
 Surveys i REDCap REDCap gør det muligt at eksponere ét eller flere instrumenter som et survey (spørgeskema) som derefter kan udfyldes direkte af patienten eller forsøgspersonen over internettet. Dette
Surveys i REDCap REDCap gør det muligt at eksponere ét eller flere instrumenter som et survey (spørgeskema) som derefter kan udfyldes direkte af patienten eller forsøgspersonen over internettet. Dette
MONOTONE POSITIVE SOLUTIONS FOR p-laplacian EQUATIONS WITH SIGN CHANGING COEFFICIENTS AND MULTI-POINT BOUNDARY CONDITIONS
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 22, No. 22, pp. 2. ISSN: 72-669. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu MONOTONE POSITIVE SOLUTIONS FOR
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 22, No. 22, pp. 2. ISSN: 72-669. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu MONOTONE POSITIVE SOLUTIONS FOR
University of Copenhagen Faculty of Science Written Exam - 3. April Algebra 3
 University of Copenhagen Faculty of Science Written Exam - 3. April 2009 Algebra 3 This exam contains 5 exercises which are to be solved in 3 hours. The exercises are posed in an English and in a Danish
University of Copenhagen Faculty of Science Written Exam - 3. April 2009 Algebra 3 This exam contains 5 exercises which are to be solved in 3 hours. The exercises are posed in an English and in a Danish
Kurver og flader Aktivitet 15 Geodætiske kurver, Isometri, Mainardi-Codazzi, Teorema Egregium
 Kurver og flader Aktivitet 15 Geodætiske kurver, Isometri, Mainardi-Codazzi, Teorema Egregium Lisbeth Fajstrup Institut for Matematiske Fag Aalborg Universitet Kurver og Flader 2013 Lisbeth Fajstrup (AAU)
Kurver og flader Aktivitet 15 Geodætiske kurver, Isometri, Mainardi-Codazzi, Teorema Egregium Lisbeth Fajstrup Institut for Matematiske Fag Aalborg Universitet Kurver og Flader 2013 Lisbeth Fajstrup (AAU)
Some results for the weighted Drazin inverse of a modified matrix
 International Journal of Applied Mathematics Computation Journal homepage: www.darbose.in/ijamc ISSN: 0974-4665 (Print) 0974-4673 (Online) Volume 6(1) 2014 1 9 Some results for the weighted Drazin inverse
International Journal of Applied Mathematics Computation Journal homepage: www.darbose.in/ijamc ISSN: 0974-4665 (Print) 0974-4673 (Online) Volume 6(1) 2014 1 9 Some results for the weighted Drazin inverse
Vores mange brugere på musskema.dk er rigtig gode til at komme med kvalificerede ønsker og behov.
 På dansk/in Danish: Aarhus d. 10. januar 2013/ the 10 th of January 2013 Kære alle Chefer i MUS-regi! Vores mange brugere på musskema.dk er rigtig gode til at komme med kvalificerede ønsker og behov. Og
På dansk/in Danish: Aarhus d. 10. januar 2013/ the 10 th of January 2013 Kære alle Chefer i MUS-regi! Vores mange brugere på musskema.dk er rigtig gode til at komme med kvalificerede ønsker og behov. Og
Chapter 6. Hydrogen Atom. 6.1 Schrödinger Equation. The Hamiltonian for a hydrogen atom is. Recall that. 1 r 2 sin 2 θ + 1. and.
 Chapter 6 Hydrogen Atom 6. Schrödinger Equation The Hamiltonian for a hydrogen atom is Recall that Ĥ = h e m e 4πɛ o r = r ) + r r r r sin θ sin θ ) + θ θ r sin θ φ and [ ˆL = h sin θ ) + )] sin θ θ θ
Chapter 6 Hydrogen Atom 6. Schrödinger Equation The Hamiltonian for a hydrogen atom is Recall that Ĥ = h e m e 4πɛ o r = r ) + r r r r sin θ sin θ ) + θ θ r sin θ φ and [ ˆL = h sin θ ) + )] sin θ θ θ
Eric Nordenstam 1 Benjamin Young 2. FPSAC 12, Nagoya, Japan
 Eric 1 Benjamin 2 1 Fakultät für Matematik Universität Wien 2 Institutionen för Matematik Royal Institute of Technology (KTH) Stockholm FPSAC 12, Nagoya, Japan The Aztec Diamond Aztec diamonds of orders
Eric 1 Benjamin 2 1 Fakultät für Matematik Universität Wien 2 Institutionen för Matematik Royal Institute of Technology (KTH) Stockholm FPSAC 12, Nagoya, Japan The Aztec Diamond Aztec diamonds of orders
A known plaintext attack on the ISAAC keystream generator
 A known plinex ck on he ISAAC keysrem generor Mrin Pudovkin mrip@online.ru Moscow Engineering Physics Insiue (Technicl Universiy) Deprmen of Crypology nd Discree Mhemics Absrc. Srem ciphers re ofen used
A known plinex ck on he ISAAC keysrem generor Mrin Pudovkin mrip@online.ru Moscow Engineering Physics Insiue (Technicl Universiy) Deprmen of Crypology nd Discree Mhemics Absrc. Srem ciphers re ofen used
Henstock-Kurzweil Laplace Transform
 Chper 5 Hensock-Kurzweil Lplce Trnsform 5.1 Inroducion The Lplce rnsform of funcion f : [, ) R, s C, is defined s he inegrl [15] e s f() d. (5.1) Mny uhors, in some previous decdes, showed heir ineres
Chper 5 Hensock-Kurzweil Lplce Trnsform 5.1 Inroducion The Lplce rnsform of funcion f : [, ) R, s C, is defined s he inegrl [15] e s f() d. (5.1) Mny uhors, in some previous decdes, showed heir ineres
User Manual for LTC IGNOU
 User Manual for LTC IGNOU 1 LTC (Leave Travel Concession) Navigation: Portal Launch HCM Application Self Service LTC Self Service 1. LTC Advance/Intimation Navigation: Launch HCM Application Self Service
User Manual for LTC IGNOU 1 LTC (Leave Travel Concession) Navigation: Portal Launch HCM Application Self Service LTC Self Service 1. LTC Advance/Intimation Navigation: Launch HCM Application Self Service
Computing the constant in Friedrichs inequality
 Computing the constant in Friedrichs inequality Tomáš Vejchodský vejchod@math.cas.cz Institute of Mathematics, Žitná 25, 115 67 Praha 1 February 8, 212, SIGA 212, Prague Motivation Classical formulation:
Computing the constant in Friedrichs inequality Tomáš Vejchodský vejchod@math.cas.cz Institute of Mathematics, Žitná 25, 115 67 Praha 1 February 8, 212, SIGA 212, Prague Motivation Classical formulation:
Help / Hjælp
 Home page Lisa & Petur www.lisapetur.dk Help / Hjælp Help / Hjælp General The purpose of our Homepage is to allow external access to pictures and videos taken/made by the Gunnarsson family. The Association
Home page Lisa & Petur www.lisapetur.dk Help / Hjælp Help / Hjælp General The purpose of our Homepage is to allow external access to pictures and videos taken/made by the Gunnarsson family. The Association
Privat-, statslig- eller regional institution m.v. Andet Added Bekaempelsesudfoerende: string No Label: Bekæmpelsesudførende
 Changes for Rottedatabasen Web Service The coming version of Rottedatabasen Web Service will have several changes some of them breaking for the exposed methods. These changes and the business logic behind
Changes for Rottedatabasen Web Service The coming version of Rottedatabasen Web Service will have several changes some of them breaking for the exposed methods. These changes and the business logic behind
Vina Nguyen HSSP July 13, 2008
 Vina Nguyen HSSP July 13, 2008 1 What does it mean if sets A, B, C are a partition of set D? 2 How do you calculate P(A B) using the formula for conditional probability? 3 What is the difference between
Vina Nguyen HSSP July 13, 2008 1 What does it mean if sets A, B, C are a partition of set D? 2 How do you calculate P(A B) using the formula for conditional probability? 3 What is the difference between
Skriftlig Eksamen Beregnelighed (DM517)
 Skriftlig Eksamen Beregnelighed (DM517) Institut for Matematik & Datalogi Syddansk Universitet Mandag den 31 Oktober 2011, kl. 9 13 Alle sædvanlige hjælpemidler (lærebøger, notater etc.) samt brug af lommeregner
Skriftlig Eksamen Beregnelighed (DM517) Institut for Matematik & Datalogi Syddansk Universitet Mandag den 31 Oktober 2011, kl. 9 13 Alle sædvanlige hjælpemidler (lærebøger, notater etc.) samt brug af lommeregner
Engelsk. Niveau D. De Merkantile Erhvervsuddannelser September Casebaseret eksamen. og
 052431_EngelskD 08/09/05 13:29 Side 1 De Merkantile Erhvervsuddannelser September 2005 Side 1 af 4 sider Casebaseret eksamen Engelsk Niveau D www.jysk.dk og www.jysk.com Indhold: Opgave 1 Presentation
052431_EngelskD 08/09/05 13:29 Side 1 De Merkantile Erhvervsuddannelser September 2005 Side 1 af 4 sider Casebaseret eksamen Engelsk Niveau D www.jysk.dk og www.jysk.com Indhold: Opgave 1 Presentation
Danish and English. Standard Field Analysis (Diderichsen) Standard Field Analysis (Diderichsen)
 Danish and English Some major poins of synacic conrass [Righ click for speaker s noes] Sandard Field nalysis (Diderichsen) Main clause able fel Forfel (Fundamenfel) Nexusfel ndholdsfel og Hvorfor Søren
Danish and English Some major poins of synacic conrass [Righ click for speaker s noes] Sandard Field nalysis (Diderichsen) Main clause able fel Forfel (Fundamenfel) Nexusfel ndholdsfel og Hvorfor Søren
The X Factor. Målgruppe. Læringsmål. Introduktion til læreren klasse & ungdomsuddannelser Engelskundervisningen
 The X Factor Målgruppe 7-10 klasse & ungdomsuddannelser Engelskundervisningen Læringsmål Eleven kan give sammenhængende fremstillinger på basis af indhentede informationer Eleven har viden om at søge og
The X Factor Målgruppe 7-10 klasse & ungdomsuddannelser Engelskundervisningen Læringsmål Eleven kan give sammenhængende fremstillinger på basis af indhentede informationer Eleven har viden om at søge og
Global attractor for the Navier Stokes equations with fractional deconvolution
 Nonlinear Differ. Equ. Appl. 5), 8 848 c 4 Springer Basel -97/5/48-38 published online December 5, 4 DOI.7/s3-4-35-y Nonlinear Differential Equations and Applications NoDEA Global attractor for the Navier
Nonlinear Differ. Equ. Appl. 5), 8 848 c 4 Springer Basel -97/5/48-38 published online December 5, 4 DOI.7/s3-4-35-y Nonlinear Differential Equations and Applications NoDEA Global attractor for the Navier
Frequency Dispersion: Dielectrics, Conductors, and Plasmas
 1/23 Frequency Dispersion: Dielectrics, Conductors, and Plasmas Carlos Felipe Espinoza Hernández Professor: Jorge Alfaro Instituto de Física Pontificia Universidad Católica de Chile 2/23 Contents 1 Simple
1/23 Frequency Dispersion: Dielectrics, Conductors, and Plasmas Carlos Felipe Espinoza Hernández Professor: Jorge Alfaro Instituto de Física Pontificia Universidad Católica de Chile 2/23 Contents 1 Simple
Our activities. Dry sales market. The assortment
 First we like to start to introduce our activities. Kébol B.V., based in the heart of the bulb district since 1989, specialises in importing and exporting bulbs world-wide. Bulbs suitable for dry sale,
First we like to start to introduce our activities. Kébol B.V., based in the heart of the bulb district since 1989, specialises in importing and exporting bulbs world-wide. Bulbs suitable for dry sale,
Hydrogen Burning in Stars-II
 ydrogen Burning in Stars-II ydrogen in induced reaction have lowest oulomb barrier highest reaction rate Reaction chain with lowest Z elements are the -chains -chains limited by weak interaction based
ydrogen Burning in Stars-II ydrogen in induced reaction have lowest oulomb barrier highest reaction rate Reaction chain with lowest Z elements are the -chains -chains limited by weak interaction based
Linear Programming ١ C H A P T E R 2
 Linear Programming ١ C H A P T E R 2 Problem Formulation Problem formulation or modeling is the process of translating a verbal statement of a problem into a mathematical statement. The Guidelines of formulation
Linear Programming ١ C H A P T E R 2 Problem Formulation Problem formulation or modeling is the process of translating a verbal statement of a problem into a mathematical statement. The Guidelines of formulation
ATEX direktivet. Vedligeholdelse af ATEX certifikater mv. Steen Christensen stec@teknologisk.dk www.atexdirektivet.
 ATEX direktivet Vedligeholdelse af ATEX certifikater mv. Steen Christensen stec@teknologisk.dk www.atexdirektivet.dk tlf: 7220 2693 Vedligeholdelse af Certifikater / tekniske dossier / overensstemmelseserklæringen.
ATEX direktivet Vedligeholdelse af ATEX certifikater mv. Steen Christensen stec@teknologisk.dk www.atexdirektivet.dk tlf: 7220 2693 Vedligeholdelse af Certifikater / tekniske dossier / overensstemmelseserklæringen.
SKRIFTLIG EKSAMEN I NUMERISK DYNAMIK Bygge- og Anlægskonstruktion, 8. semester Fredag den 30. juni 2005, kl Alle hjælpemidler er tilladt
 SKRIFTLIG EKSAMEN I NUMERISK DYNAMIK Bygge- og Anlægskonstruktion, 8. semester Fredag den 3. juni 5, kl. 8.3-.3 Alle hjælpemidler er tilladt OPGAVE u = y B u = u C A x c u = D u = Figuren viser en homogen
SKRIFTLIG EKSAMEN I NUMERISK DYNAMIK Bygge- og Anlægskonstruktion, 8. semester Fredag den 3. juni 5, kl. 8.3-.3 Alle hjælpemidler er tilladt OPGAVE u = y B u = u C A x c u = D u = Figuren viser en homogen
Skriftlig Eksamen Kombinatorik, Sandsynlighed og Randomiserede Algoritmer (DM528)
 Skriftlig Eksamen Kombinatorik, Sandsynlighed og Randomiserede Algoritmer (DM58) Institut for Matematik og Datalogi Syddansk Universitet, Odense Torsdag den 1. januar 01 kl. 9 13 Alle sædvanlige hjælpemidler
Skriftlig Eksamen Kombinatorik, Sandsynlighed og Randomiserede Algoritmer (DM58) Institut for Matematik og Datalogi Syddansk Universitet, Odense Torsdag den 1. januar 01 kl. 9 13 Alle sædvanlige hjælpemidler
Info og krav til grupper med motorkøjetøjer
 Info og krav til grupper med motorkøjetøjer (English version, see page 4) GENERELT - FOR ALLE TYPER KØRETØJER ØJER GODT MILJØ FOR ALLE Vi ønsker at paraden er en god oplevelse for alle deltagere og tilskuere,
Info og krav til grupper med motorkøjetøjer (English version, see page 4) GENERELT - FOR ALLE TYPER KØRETØJER ØJER GODT MILJØ FOR ALLE Vi ønsker at paraden er en god oplevelse for alle deltagere og tilskuere,
Positive solutions of Kirchhoff type elliptic equations involving a critical Sobolev exponent
 Nonlinear Differ. Equ. Appl. 1 (014, 885 914 c 014 Springer Basel 101-97/14/060885-30 published online April 18, 014 DOI 10.1007/s00030-014-071-4 Nonlinear Differential Equations and Applications NoDEA
Nonlinear Differ. Equ. Appl. 1 (014, 885 914 c 014 Springer Basel 101-97/14/060885-30 published online April 18, 014 DOI 10.1007/s00030-014-071-4 Nonlinear Differential Equations and Applications NoDEA
264.. Cox, Daio Jang (23) Grandell (1976). 1.1 (Ω, F, {F, [, ]}, P). N λ, λ F, 1 2 u R, λ d < a... E{e iu(n 2 N 1 ) F λ 2 } = e {(eiu 1) 2 1 λ d}, F λ
![264.. Cox, Daio Jang (23) Grandell (1976). 1.1 (Ω, F, {F, [, ]}, P). N λ, λ F, 1 2 u R, λ d < a... E{e iu(n 2 N 1 ) F λ 2 } = e {(eiu 1) 2 1 λ d}, F λ 264.. Cox, Daio Jang (23) Grandell (1976). 1.1 (Ω, F, {F, [, ]}, P). N λ, λ F, 1 2 u R, λ d < a... E{e iu(n 2 N 1 ) F λ 2 } = e {(eiu 1) 2 1 λ d}, F λ](/thumbs/92/110314096.jpg) 212 6 Chinee Journal of Applied Probabiliy and Saiic Vol.28 No.3 Jun. 212 Lévy (,, 2156),, Lévy.., (Credi Defaul Swap). :,,,. : O211.6. 1.,.,.,,.,, O Kane urnbull (23), Jamhidian (24), Crepey, Jeanblanc
212 6 Chinee Journal of Applied Probabiliy and Saiic Vol.28 No.3 Jun. 212 Lévy (,, 2156),, Lévy.., (Credi Defaul Swap). :,,,. : O211.6. 1.,.,.,,.,, O Kane urnbull (23), Jamhidian (24), Crepey, Jeanblanc
UNISONIC TECHNOLOGIES CO.,
 UNISONIC TECHNOLOGIES CO., 3 TERMINAL 1A NEGATIVE VOLTAGE REGULATOR DESCRIPTION 1 TO-263 The UTC series of three-terminal negative regulators are available in TO-263 package and with several fixed output
UNISONIC TECHNOLOGIES CO., 3 TERMINAL 1A NEGATIVE VOLTAGE REGULATOR DESCRIPTION 1 TO-263 The UTC series of three-terminal negative regulators are available in TO-263 package and with several fixed output
University of Copenhagen Faculty of Science Written Exam - 8. April 2008. Algebra 3
 University of Copenhagen Faculty of Science Written Exam - 8. April 2008 Algebra 3 This exam contains 5 exercises which are to be solved in 3 hours. The exercises are posed in an English and in a Danish
University of Copenhagen Faculty of Science Written Exam - 8. April 2008 Algebra 3 This exam contains 5 exercises which are to be solved in 3 hours. The exercises are posed in an English and in a Danish
Engelsk. Niveau C. De Merkantile Erhvervsuddannelser September 2005. Casebaseret eksamen. www.jysk.dk og www.jysk.com.
 052430_EngelskC 08/09/05 13:29 Side 1 De Merkantile Erhvervsuddannelser September 2005 Side 1 af 4 sider Casebaseret eksamen Engelsk Niveau C www.jysk.dk og www.jysk.com Indhold: Opgave 1 Presentation
052430_EngelskC 08/09/05 13:29 Side 1 De Merkantile Erhvervsuddannelser September 2005 Side 1 af 4 sider Casebaseret eksamen Engelsk Niveau C www.jysk.dk og www.jysk.com Indhold: Opgave 1 Presentation
Skriftlig Eksamen Beregnelighed (DM517)
 Skriftlig Eksamen Beregnelighed (DM517) Institut for Matematik & Datalogi Syddansk Universitet Mandag den 7 Januar 2008, kl. 9 13 Alle sædvanlige hjælpemidler (lærebøger, notater etc.) samt brug af lommeregner
Skriftlig Eksamen Beregnelighed (DM517) Institut for Matematik & Datalogi Syddansk Universitet Mandag den 7 Januar 2008, kl. 9 13 Alle sædvanlige hjælpemidler (lærebøger, notater etc.) samt brug af lommeregner
Curve Modeling B-Spline Curves. Dr. S.M. Malaek. Assistant: M. Younesi
 Curve Modeling B-Spline Curves Dr. S.M. Malaek Assistant: M. Younesi Motivation B-Spline Basis: Motivation Consider designing the profile of a vase. The left figure below is a Bézier curve of degree 11;
Curve Modeling B-Spline Curves Dr. S.M. Malaek Assistant: M. Younesi Motivation B-Spline Basis: Motivation Consider designing the profile of a vase. The left figure below is a Bézier curve of degree 11;
Eksamen i Signalbehandling og matematik
 Opgave. (%).a. Figur og afbilleder et diskret tid signal [n ] og dets DTFT. [n] bruges som input til et LTI filter med en frekvens amplitude respons som vist på figur. Hvilket af de 4 output signaler (y
Opgave. (%).a. Figur og afbilleder et diskret tid signal [n ] og dets DTFT. [n] bruges som input til et LTI filter med en frekvens amplitude respons som vist på figur. Hvilket af de 4 output signaler (y
On the Relations Between Fuzzy Topologies and α Cut Topologies
 S Ü Fen Ed Fak Fen Derg Sayı 23 (2004) 21-27, KONYA On the Relations Between Fuzzy Topologies and α Cut Topologies Zekeriya GÜNEY 1 Abstract: In this study, some relations have been generated between fuzzy
S Ü Fen Ed Fak Fen Derg Sayı 23 (2004) 21-27, KONYA On the Relations Between Fuzzy Topologies and α Cut Topologies Zekeriya GÜNEY 1 Abstract: In this study, some relations have been generated between fuzzy
CHAPTER 8: USING OBJECTS
 Ruby: Philosophy & Implementation CHAPTER 8: USING OBJECTS Introduction to Computer Science Using Ruby Ruby is the latest in the family of Object Oriented Programming Languages As such, its designer studied
Ruby: Philosophy & Implementation CHAPTER 8: USING OBJECTS Introduction to Computer Science Using Ruby Ruby is the latest in the family of Object Oriented Programming Languages As such, its designer studied
Trolling Master Bornholm 2016 Nyhedsbrev nr. 3
 Trolling Master Bornholm 2016 Nyhedsbrev nr. 3 English version further down Den første dag i Bornholmerlaks konkurrencen Formanden for Bornholms Trollingklub, Anders Schou Jensen (og meddomer i TMB) fik
Trolling Master Bornholm 2016 Nyhedsbrev nr. 3 English version further down Den første dag i Bornholmerlaks konkurrencen Formanden for Bornholms Trollingklub, Anders Schou Jensen (og meddomer i TMB) fik
Combined concave convex effects in anisotropic elliptic equations with variable exponent
 Nonlinear Differ. Equ. Appl. 22 (205), 39 40 c 204 Springer Basel 02-9722/5/03039-20 published online October 4, 204 DOI 0.007/s00030-04-0288-8 Nonlinear Differential Equations and Applications NoDEA Combined
Nonlinear Differ. Equ. Appl. 22 (205), 39 40 c 204 Springer Basel 02-9722/5/03039-20 published online October 4, 204 DOI 0.007/s00030-04-0288-8 Nonlinear Differential Equations and Applications NoDEA Combined
Pattern formation Turing instability
 Pattern formation Turing instability Tomáš Vejchodský Centre for Mathematical Biology Mathematical Institute Summer school, Prague, 6 8 August, 213 Outline Motivation Turing instability general conditions
Pattern formation Turing instability Tomáš Vejchodský Centre for Mathematical Biology Mathematical Institute Summer school, Prague, 6 8 August, 213 Outline Motivation Turing instability general conditions
E-PAD Bluetooth hængelås E-PAD Bluetooth padlock E-PAD Bluetooth Vorhängeschloss
 E-PAD Bluetooth hængelås E-PAD Bluetooth padlock E-PAD Bluetooth Vorhängeschloss Brugervejledning (side 2-6) Userguide (page 7-11) Bedienungsanleitung 1 - Hvordan forbinder du din E-PAD hængelås med din
E-PAD Bluetooth hængelås E-PAD Bluetooth padlock E-PAD Bluetooth Vorhängeschloss Brugervejledning (side 2-6) Userguide (page 7-11) Bedienungsanleitung 1 - Hvordan forbinder du din E-PAD hængelås med din
Strings and Sets: set complement, union, intersection, etc. set concatenation AB, power of set A n, A, A +
 Strings and Sets: A string over Σ is any nite-length sequence of elements of Σ The set of all strings over alphabet Σ is denoted as Σ Operators over set: set complement, union, intersection, etc. set concatenation
Strings and Sets: A string over Σ is any nite-length sequence of elements of Σ The set of all strings over alphabet Σ is denoted as Σ Operators over set: set complement, union, intersection, etc. set concatenation
MultiProgrammer Manual
 MultiProgrammer Manual MultiProgrammeren bruges til at læse og skrive værdier til ModBus register i LS Controls frekvensomformer E 1045. Dansk Version side 2 til 4 The MultiProgrammer is used for the writing
MultiProgrammer Manual MultiProgrammeren bruges til at læse og skrive værdier til ModBus register i LS Controls frekvensomformer E 1045. Dansk Version side 2 til 4 The MultiProgrammer is used for the writing
Statistik for MPH: 7
 Statistik for MPH: 7 3. november 2011 www.biostat.ku.dk/~pka/mph11 Attributable risk, bestemmelse af stikprøvestørrelse (Silva: 333-365, 381-383) Per Kragh Andersen 1 Fra den 6. uges statistikundervisning:
Statistik for MPH: 7 3. november 2011 www.biostat.ku.dk/~pka/mph11 Attributable risk, bestemmelse af stikprøvestørrelse (Silva: 333-365, 381-383) Per Kragh Andersen 1 Fra den 6. uges statistikundervisning:
Pontryagin Approximations for Optimal Design of Elastic Structures
 Pontryagin Approximations for Optimal Design of Elastic Structures Jesper Carlsson NADA, KTH jesperc@nada.kth.se Collaborators: Anders Szepessy, Mattias Sandberg October 5, 2005 A typical optimal design
Pontryagin Approximations for Optimal Design of Elastic Structures Jesper Carlsson NADA, KTH jesperc@nada.kth.se Collaborators: Anders Szepessy, Mattias Sandberg October 5, 2005 A typical optimal design
19.3. Second Order ODEs. Introduction. Prerequisites. Learning Outcomes
 Second Order ODEs 19.3 Introduction In this Section we start to learn how to solve second-order differential equations of a particular type: those that are linear and that have constant coefficients. Such
Second Order ODEs 19.3 Introduction In this Section we start to learn how to solve second-order differential equations of a particular type: those that are linear and that have constant coefficients. Such
Hermite-Hadamard-Fejer Type Inequalities for s Convex Function in the Second Sense via Fractional Integrals
 Filom 30: 06), 33 338 DOI 0.98/FIL63S Published by Fculy o Sciences nd Mhemics, Universiy o Niš, Serbi Avilble : hp://www.pm.ni.c.rs/ilom Hermie-Hdmrd-Fejer Type Ineuliies or s Convex Funcion in he Second
Filom 30: 06), 33 338 DOI 0.98/FIL63S Published by Fculy o Sciences nd Mhemics, Universiy o Niš, Serbi Avilble : hp://www.pm.ni.c.rs/ilom Hermie-Hdmrd-Fejer Type Ineuliies or s Convex Funcion in he Second
Trolling Master Bornholm 2012
 Trolling Master Bornholm 1 (English version further down) Tak for denne gang Det var en fornøjelse især jo også fordi vejret var med os. Så heldig har vi aldrig været før. Vi skal evaluere 1, og I må meget
Trolling Master Bornholm 1 (English version further down) Tak for denne gang Det var en fornøjelse især jo også fordi vejret var med os. Så heldig har vi aldrig været før. Vi skal evaluere 1, og I må meget
Skriftlig Eksamen Automatteori og Beregnelighed (DM17)
 Skriftlig Eksamen Automatteori og Beregnelighed (DM17) Institut for Matematik & Datalogi Syddansk Universitet Odense Campus Lørdag, den 15. Januar 2005 Alle sædvanlige hjælpemidler (lærebøger, notater
Skriftlig Eksamen Automatteori og Beregnelighed (DM17) Institut for Matematik & Datalogi Syddansk Universitet Odense Campus Lørdag, den 15. Januar 2005 Alle sædvanlige hjælpemidler (lærebøger, notater
Satisability of Boolean Formulas
 SAT exercises 1 March, 2016 slide 1 Satisability of Boolean Formulas Combinatorics and Algorithms Prof. Emo Welzl Assistant: (CAB G36.1, cannamalai@inf.ethz.ch) URL: http://www.ti.inf.ethz.ch/ew/courses/sat16/
SAT exercises 1 March, 2016 slide 1 Satisability of Boolean Formulas Combinatorics and Algorithms Prof. Emo Welzl Assistant: (CAB G36.1, cannamalai@inf.ethz.ch) URL: http://www.ti.inf.ethz.ch/ew/courses/sat16/
Adaptive Algorithms for Blind Separation of Dependent Sources. George V. Moustakides INRIA, Sigma 2
 Adaptive Algorithms for Blind Separation of Dependent Sources George V. Moustakides INRIA, Sigma 2 Problem definition-motivation Existing adaptive scheme-independence General adaptive scheme-dependence
Adaptive Algorithms for Blind Separation of Dependent Sources George V. Moustakides INRIA, Sigma 2 Problem definition-motivation Existing adaptive scheme-independence General adaptive scheme-dependence
Brug sømbrættet til at lave sjove figurer. Lav fx: Få de andre til at gætte, hvad du har lavet. Use the nail board to make funny shapes.
 Brug sømbrættet til at lave sjove figurer. Lav f: Et dannebrogsflag Et hus med tag, vinduer og dør En fugl En bil En blomst Få de andre til at gætte, hvad du har lavet. Use the nail board to make funn
Brug sømbrættet til at lave sjove figurer. Lav f: Et dannebrogsflag Et hus med tag, vinduer og dør En fugl En bil En blomst Få de andre til at gætte, hvad du har lavet. Use the nail board to make funn
Particle-based T-Spline Level Set Evolution for 3D Object Reconstruction with Range and Volume Constraints
 Particle-based T-Spline Level Set for 3D Object Reconstruction with Range and Volume Constraints Robert Feichtinger (joint work with Huaiping Yang, Bert Jüttler) Institute of Applied Geometry, JKU Linz
Particle-based T-Spline Level Set for 3D Object Reconstruction with Range and Volume Constraints Robert Feichtinger (joint work with Huaiping Yang, Bert Jüttler) Institute of Applied Geometry, JKU Linz
INTERVAL VALUED FUZZY IDEALS OF GAMMA NEAR-RINGS
 BULLETIN OF THE INTERNATIONAL MATHEMATICAL VIRTUAL INSTITUTE ISSN (p) 2303-4874, ISSN (o) 2303-4955 www.imvibl.org /JOURNALS / BULLETIN Vol. 8(2018), 301-314 DOI: 10.7251/BIMVI1802301C Former BULLETIN
BULLETIN OF THE INTERNATIONAL MATHEMATICAL VIRTUAL INSTITUTE ISSN (p) 2303-4874, ISSN (o) 2303-4955 www.imvibl.org /JOURNALS / BULLETIN Vol. 8(2018), 301-314 DOI: 10.7251/BIMVI1802301C Former BULLETIN
Extended quasi-homogeneous polynomial system in R 3
 Nonlinear Differ. Equ. Appl. 2 213, 1771 1794 c 213 Springer Basel 121-9722/13/61771-24 published online May 1, 213 DOI 1.17/s3-13-23-5 Nonlinear Differential Equations and Applications NoDEA Extended
Nonlinear Differ. Equ. Appl. 2 213, 1771 1794 c 213 Springer Basel 121-9722/13/61771-24 published online May 1, 213 DOI 1.17/s3-13-23-5 Nonlinear Differential Equations and Applications NoDEA Extended
Læs venligst Beboer information om projekt vandskade - sikring i 2015/2016
 Læs venligst Beboer information om projekt vandskade - sikring i 2015/2016 Vi er nødsaget til at få adgang til din lejlighed!! Hvis Kridahl (VVS firma) har bedt om adgang til din/jeres lejlighed og nøgler,
Læs venligst Beboer information om projekt vandskade - sikring i 2015/2016 Vi er nødsaget til at få adgang til din lejlighed!! Hvis Kridahl (VVS firma) har bedt om adgang til din/jeres lejlighed og nøgler,
Agenda. The need to embrace our complex health care system and learning to do so. Christian von Plessen Contributors to healthcare services in Denmark
 Agenda The need to embrace our complex health care system and learning to do so. Christian von Plessen Contributors to healthcare services in Denmark Colitis and Crohn s association Denmark. Charlotte
Agenda The need to embrace our complex health care system and learning to do so. Christian von Plessen Contributors to healthcare services in Denmark Colitis and Crohn s association Denmark. Charlotte
Black Jack --- Review. Spring 2012
 Black Jack --- Review Spring 2012 Simulation Simulation can solve real-world problems by modeling realworld processes to provide otherwise unobtainable information. Computer simulation is used to predict
Black Jack --- Review Spring 2012 Simulation Simulation can solve real-world problems by modeling realworld processes to provide otherwise unobtainable information. Computer simulation is used to predict
Project Step 7. Behavioral modeling of a dual ported register set. 1/8/ L11 Project Step 5 Copyright Joanne DeGroat, ECE, OSU 1
 Project Step 7 Behavioral modeling of a dual ported register set. Copyright 2006 - Joanne DeGroat, ECE, OSU 1 The register set Register set specifications 16 dual ported registers each with 16- bit words
Project Step 7 Behavioral modeling of a dual ported register set. Copyright 2006 - Joanne DeGroat, ECE, OSU 1 The register set Register set specifications 16 dual ported registers each with 16- bit words
Additive Property of Drazin Invertibility of Elements in a Ring
 Filomat 30:5 (2016), 1185 1193 DOI 10.2298/FIL1605185W Published by Faculty of Sciences and Mathematics, University of Niš, Serbia Available at: http://www.pmf.ni.ac.rs/filomat Additive Property of Drazin
Filomat 30:5 (2016), 1185 1193 DOI 10.2298/FIL1605185W Published by Faculty of Sciences and Mathematics, University of Niš, Serbia Available at: http://www.pmf.ni.ac.rs/filomat Additive Property of Drazin
Userguide. NN Markedsdata. for. Microsoft Dynamics CRM 2011. v. 1.0
 Userguide NN Markedsdata for Microsoft Dynamics CRM 2011 v. 1.0 NN Markedsdata www. Introduction Navne & Numre Web Services for Microsoft Dynamics CRM hereafter termed NN-DynCRM enable integration to Microsoft
Userguide NN Markedsdata for Microsoft Dynamics CRM 2011 v. 1.0 NN Markedsdata www. Introduction Navne & Numre Web Services for Microsoft Dynamics CRM hereafter termed NN-DynCRM enable integration to Microsoft
Statistik for MPH: oktober Attributable risk, bestemmelse af stikprøvestørrelse (Silva: , )
 Statistik for MPH: 7 29. oktober 2015 www.biostat.ku.dk/~pka/mph15 Attributable risk, bestemmelse af stikprøvestørrelse (Silva: 333-365, 381-383) Per Kragh Andersen 1 Fra den 6. uges statistikundervisning:
Statistik for MPH: 7 29. oktober 2015 www.biostat.ku.dk/~pka/mph15 Attributable risk, bestemmelse af stikprøvestørrelse (Silva: 333-365, 381-383) Per Kragh Andersen 1 Fra den 6. uges statistikundervisning:
The purpose of our Homepage is to allow external access to pictures and videos taken/made by the Gunnarsson family.
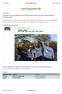 General The purpose of our Homepage is to allow external access to pictures and videos taken/made by the Gunnarsson family. Formålet med vores hjemmesiden er at gøre billeder og video som vi (Gunnarsson)
General The purpose of our Homepage is to allow external access to pictures and videos taken/made by the Gunnarsson family. Formålet med vores hjemmesiden er at gøre billeder og video som vi (Gunnarsson)
Skriftlig Eksamen Diskret matematik med anvendelser (DM72)
 Skriftlig Eksamen Diskret matematik med anvendelser (DM72) Institut for Matematik & Datalogi Syddansk Universitet, Odense Onsdag den 18. januar 2006 Alle sædvanlige hjælpemidler (lærebøger, notater etc.),
Skriftlig Eksamen Diskret matematik med anvendelser (DM72) Institut for Matematik & Datalogi Syddansk Universitet, Odense Onsdag den 18. januar 2006 Alle sædvanlige hjælpemidler (lærebøger, notater etc.),
ECE 551: Digital System * Design & Synthesis Lecture Set 5
 ECE 551: Digital System * Design & Synthesis Lecture Set 5 5.1: Verilog Behavioral Model for Finite State Machines (FSMs) 5.2: Verilog Simulation I/O and 2001 Standard (In Separate File) 3/4/2003 1 ECE
ECE 551: Digital System * Design & Synthesis Lecture Set 5 5.1: Verilog Behavioral Model for Finite State Machines (FSMs) 5.2: Verilog Simulation I/O and 2001 Standard (In Separate File) 3/4/2003 1 ECE
Aristoteles Camillo. To cite this version: HAL Id: hal
 An experimentally-based modeling study of the effect of anti-angiogenic therapies on primary tumor kinetics for data analysis of clinically relevant animal models of metastasis Aristoteles Camillo To cite
An experimentally-based modeling study of the effect of anti-angiogenic therapies on primary tumor kinetics for data analysis of clinically relevant animal models of metastasis Aristoteles Camillo To cite
DET KONGELIGE BIBLIOTEK NATIONALBIBLIOTEK OG KØBENHAVNS UNIVERSITETS- BIBLIOTEK. Index
 DET KONGELIGE Index Download driver... 2 Find the Windows 7 version.... 2 Download the Windows Vista driver.... 4 Extract driver... 5 Windows Vista installation of a printer.... 7 Side 1 af 12 DET KONGELIGE
DET KONGELIGE Index Download driver... 2 Find the Windows 7 version.... 2 Download the Windows Vista driver.... 4 Extract driver... 5 Windows Vista installation of a printer.... 7 Side 1 af 12 DET KONGELIGE
FAST FORRETNINGSSTED FAST FORRETNINGSSTED I DANSK PRAKSIS
 FAST FORRETNINGSSTED FAST FORRETNINGSSTED I DANSK PRAKSIS SKM2012.64.SR FORRETNINGSSTED I LUXEMBOURG En dansk udbyder af internet-spil ønsker at etablere et fast forretningssted i Luxembourg: Scenarier:
FAST FORRETNINGSSTED FAST FORRETNINGSSTED I DANSK PRAKSIS SKM2012.64.SR FORRETNINGSSTED I LUXEMBOURG En dansk udbyder af internet-spil ønsker at etablere et fast forretningssted i Luxembourg: Scenarier:
Bookingmuligheder for professionelle brugere i Dansehallerne 2015-16
 Bookingmuligheder for professionelle brugere i Dansehallerne 2015-16 Modtager man økonomisk støtte til et danseprojekt, har en premieredato og er professionel bruger af Dansehallerne har man mulighed for
Bookingmuligheder for professionelle brugere i Dansehallerne 2015-16 Modtager man økonomisk støtte til et danseprojekt, har en premieredato og er professionel bruger af Dansehallerne har man mulighed for
Nodal set of strongly competition systems with fractional Laplacian
 Nonlinear Differ. Equ. Appl. 22 (2015), 1483 1513 c 2015 Springer Basel 1021-9722/15/051483-31 published online June 2, 2015 DOI 10.1007/s00030-015-0332-3 Nonlinear Differential Equations and Applications
Nonlinear Differ. Equ. Appl. 22 (2015), 1483 1513 c 2015 Springer Basel 1021-9722/15/051483-31 published online June 2, 2015 DOI 10.1007/s00030-015-0332-3 Nonlinear Differential Equations and Applications
IBM Network Station Manager. esuite 1.5 / NSM Integration. IBM Network Computer Division. tdc - 02/08/99 lotusnsm.prz Page 1
 IBM Network Station Manager esuite 1.5 / NSM Integration IBM Network Computer Division tdc - 02/08/99 lotusnsm.prz Page 1 New esuite Settings in NSM The Lotus esuite Workplace administration option is
IBM Network Station Manager esuite 1.5 / NSM Integration IBM Network Computer Division tdc - 02/08/99 lotusnsm.prz Page 1 New esuite Settings in NSM The Lotus esuite Workplace administration option is
Angle Ini/al side Terminal side Vertex Standard posi/on Posi/ve angles Nega/ve angles. Quadrantal angle
 Mrs. Valentine AFM Objective: I will be able to identify angle types, convert between degrees and radians for angle measures, identify coterminal angles, find the length of an intercepted arc, and find
Mrs. Valentine AFM Objective: I will be able to identify angle types, convert between degrees and radians for angle measures, identify coterminal angles, find the length of an intercepted arc, and find
Nyhedsmail, december 2013 (scroll down for English version)
 Nyhedsmail, december 2013 (scroll down for English version) Kære Omdeler Julen venter rundt om hjørnet. Og netop julen er årsagen til, at NORDJYSKE Distributions mange omdelere har ekstra travlt med at
Nyhedsmail, december 2013 (scroll down for English version) Kære Omdeler Julen venter rundt om hjørnet. Og netop julen er årsagen til, at NORDJYSKE Distributions mange omdelere har ekstra travlt med at
Richter 2013 Presentation Mentor: Professor Evans Philosophy Department Taylor Henderson May 31, 2013
 Richter 2013 Presentation Mentor: Professor Evans Philosophy Department Taylor Henderson May 31, 2013 OVERVIEW I m working with Professor Evans in the Philosophy Department on his own edition of W.E.B.
Richter 2013 Presentation Mentor: Professor Evans Philosophy Department Taylor Henderson May 31, 2013 OVERVIEW I m working with Professor Evans in the Philosophy Department on his own edition of W.E.B.
GUIDE TIL BREVSKRIVNING
 GUIDE TIL BREVSKRIVNING APPELBREVE Formålet med at skrive et appelbrev er at få modtageren til at overholde menneskerettighederne. Det er en god idé at lægge vægt på modtagerens forpligtelser over for
GUIDE TIL BREVSKRIVNING APPELBREVE Formålet med at skrive et appelbrev er at få modtageren til at overholde menneskerettighederne. Det er en god idé at lægge vægt på modtagerens forpligtelser over for
what is this all about? Introduction three-phase diode bridge rectifier input voltages input voltages, waveforms normalization of voltages voltages?
 what is this all about? v A Introduction three-phase diode bridge rectifier D1 D D D4 D5 D6 i OUT + v OUT v B i 1 i i + + + v 1 v v input voltages input voltages, waveforms v 1 = V m cos ω 0 t v = V m
what is this all about? v A Introduction three-phase diode bridge rectifier D1 D D D4 D5 D6 i OUT + v OUT v B i 1 i i + + + v 1 v v input voltages input voltages, waveforms v 1 = V m cos ω 0 t v = V m
Appendix 1: Interview guide Maria og Kristian Lundgaard-Karlshøj, Ausumgaard
 Appendix 1: Interview guide Maria og Kristian Lundgaard-Karlshøj, Ausumgaard Fortæl om Ausumgaard s historie Der er hele tiden snak om værdier, men hvad er det for nogle værdier? uddyb forklar definer
Appendix 1: Interview guide Maria og Kristian Lundgaard-Karlshøj, Ausumgaard Fortæl om Ausumgaard s historie Der er hele tiden snak om værdier, men hvad er det for nogle værdier? uddyb forklar definer
De tre høringssvar findes til sidst i dette dokument (Bilag 1, 2 og 3). I forlængelse af de indkomne kommentarer bemærkes følgende:
 NOTAT VEDR. HØRINGSSVAR København 2018.10.26 BAGGRUND: Kommunalbestyrelsen i Frederiksberg Kommune vedtog den 18. april 2016 at igangsætte processen omkring etablering af et fælles gårdanlæg i karré 41,
NOTAT VEDR. HØRINGSSVAR København 2018.10.26 BAGGRUND: Kommunalbestyrelsen i Frederiksberg Kommune vedtog den 18. april 2016 at igangsætte processen omkring etablering af et fælles gårdanlæg i karré 41,
On the viscosity solutions to Trudinger s equation
 Nonlinear Differ. Equ. Appl. 22 (2015), 1089 1114 c 2015 Springer Basel 1021-9722/15/051089-26 published online March 12, 2015 DOI 10.1007/s00030-015-0315-4 Nonlinear Differential Equations and Applications
Nonlinear Differ. Equ. Appl. 22 (2015), 1089 1114 c 2015 Springer Basel 1021-9722/15/051089-26 published online March 12, 2015 DOI 10.1007/s00030-015-0315-4 Nonlinear Differential Equations and Applications
Boligsøgning / Search for accommodation!
 Boligsøgning / Search for accommodation! For at guide dig frem til den rigtige vejledning, skal du lige svare på et par spørgsmål: To make sure you are using the correct guide for applying you must answer
Boligsøgning / Search for accommodation! For at guide dig frem til den rigtige vejledning, skal du lige svare på et par spørgsmål: To make sure you are using the correct guide for applying you must answer
Resource types R 1 1, R 2 2,..., R m CPU cycles, memory space, files, I/O devices Each resource type R i has W i instances.
 System Model Resource types R 1 1, R 2 2,..., R m CPU cycles, memory space, files, I/O devices Each resource type R i has W i instances. Each process utilizes a resource as follows: request use e.g., request
System Model Resource types R 1 1, R 2 2,..., R m CPU cycles, memory space, files, I/O devices Each resource type R i has W i instances. Each process utilizes a resource as follows: request use e.g., request
